Mycobacterial DNA polymerase I: activities and crystal structures of the POL domain as apoenzyme and in complex with a DNA primer-template and of the full-length FEN/EXO-POL enzyme.
Ghosh, S., Goldgur, Y., Shuman, S.(2020) Nucleic Acids Res 48: 3165-3180
- PubMed: 32034423
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa075
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6VDC, 6VDD, 6VDE - PubMed Abstract:
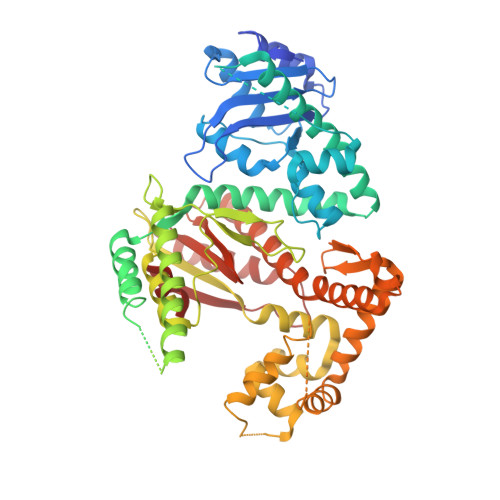
Mycobacterial Pol1 is a bifunctional enzyme composed of an N-terminal DNA flap endonuclease/5' exonuclease domain (FEN/EXO) and a C-terminal DNA polymerase domain (POL). Here we document additional functions of Pol1: FEN activity on the flap RNA strand of an RNA:DNA hybrid and reverse transcriptase activity on a DNA-primed RNA template. We report crystal structures of the POL domain, as apoenzyme and as ternary complex with 3'-dideoxy-terminated DNA primer-template and dNTP. The thumb, palm, and fingers subdomains of POL form an extensive interface with the primer-template and the triphosphate of the incoming dNTP. Progression from an open conformation of the apoenzyme to a nearly closed conformation of the ternary complex entails a disordered-to-ordered transition of several segments of the thumb and fingers modules and an inward motion of the fingers subdomain-especially the O helix-to engage the primer-template and dNTP triphosphate. Distinctive structural features of mycobacterial Pol1 POL include a manganese binding site in the vestigial 3' exonuclease subdomain and a non-catalytic water-bridged magnesium complex at the protein-DNA interface. We report a crystal structure of the bifunctional FEN/EXO-POL apoenzyme that reveals the positions of two active site metals in the FEN/EXO domain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Biology Program, Sloan-Kettering Institute, New York, NY 10065, USA.