Structural features of human inositol phosphate multikinase rationalize its inositol phosphate kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase activities.
Wang, H., Shears, S.B.(2017) J Biol Chem 292: 18192-18202
- PubMed: 28882892
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.801845
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
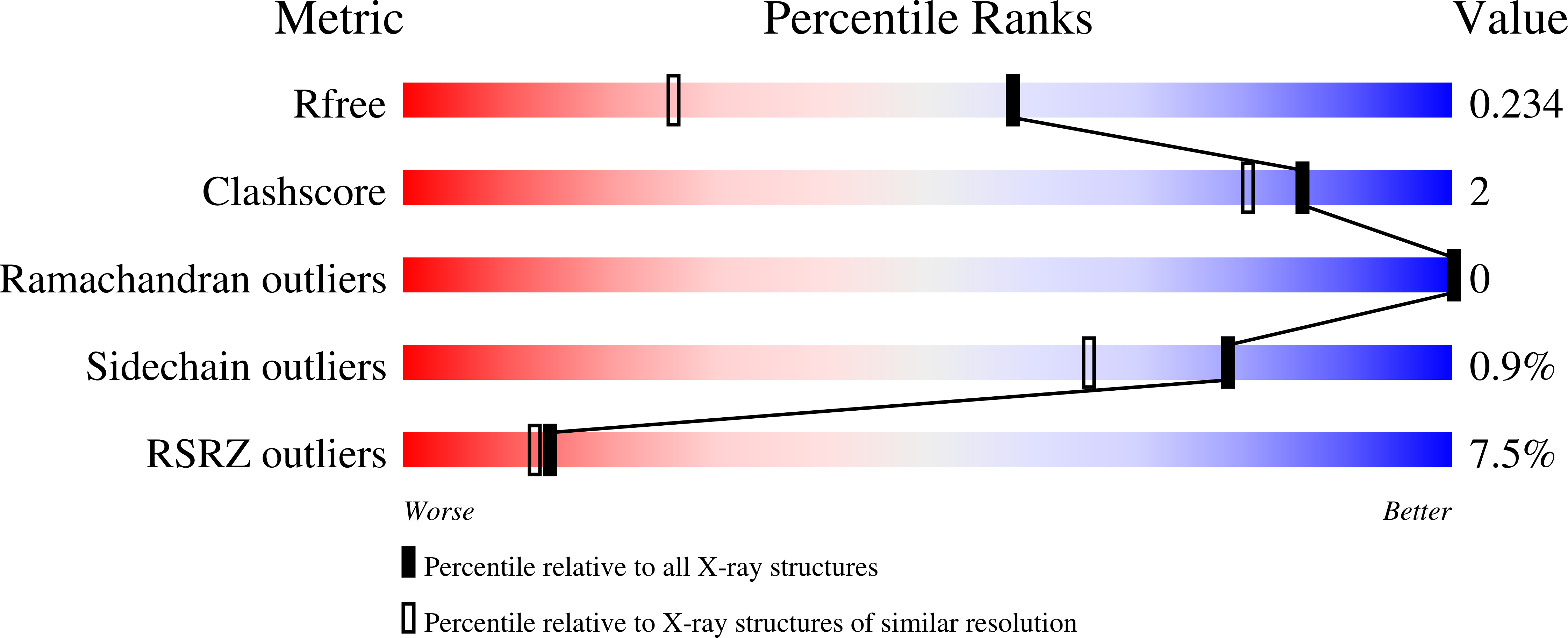
5W2G, 5W2H, 5W2I - PubMed Abstract:
Human inositol phosphate multikinase ( Hs IPMK) critically contributes to intracellular signaling through its inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P 3 ) 3-kinase and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P 2 ) 3-kinase activities. This catalytic profile is not conserved; orthologs from Arabidopsis thaliana and Saccharomyces cerevisiae are predominantly Ins(1,4,5)P 3 6-kinases, and the plant enzyme cannot phosphorylate PtdIns(4,5)P 2 Therefore, crystallographic analysis of the yeast and plant enzymes, without bound inositol phosphates, do not structurally rationalize Hs IPMK activities. Here, we present 1.6-Å resolution crystal structures of Hs IPMK in complex with either Ins(1,4,5)P 3 or PtdIns(4,5)P 2 The Ins(1,4,5)P 3 headgroup of PtdIns(4,5)P 2 binds in precisely the same orientation as free Ins(1,4,5)P 3 itself, indicative of evolutionary optimization of 3-kinase activities against both substrates. We report on nucleotide binding between the separate N- and C-lobes of Hs IPMK. The N-lobe exhibits a remarkable degree of conservation with protein kinase A (root mean square deviation = 1.8 Å), indicating common ancestry. We also describe structural features unique to Hs IPMK. First, we observed a constrained, horseshoe-shaped substrate pocket, formed from an α-helix, a 3 10 helix, and a recently evolved tri-proline loop. We further found Hs IPMK activities rely on a preponderance of Gln residues, in contrast to the larger Lys and Arg residues in yeast and plant orthologs. These conclusions are supported by analyzing 14 single-site Hs IPMK mutants, some of which differentially affect 3-kinase and 6-kinase activities. Overall, we structurally rationalize phosphorylation of Ins(1,4,5)P 3 and PtdIns(4,5)P 2 by Hs IPMK.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Inositol Signaling Group, Signal Transduction Laboratory, NIEHS, National Institutes of Health, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27709 wangh7@niehs.nih.gov.