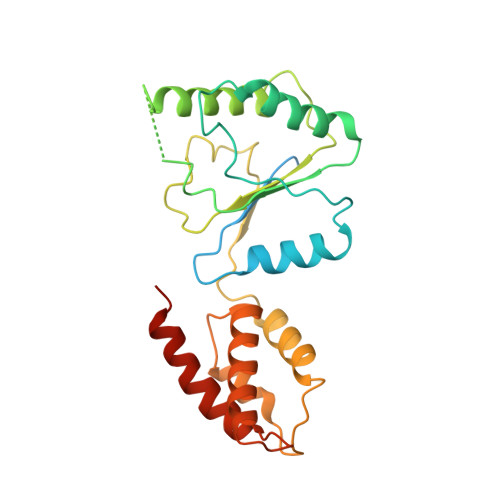
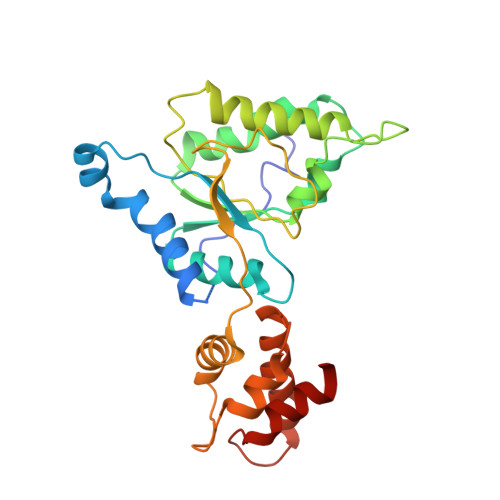
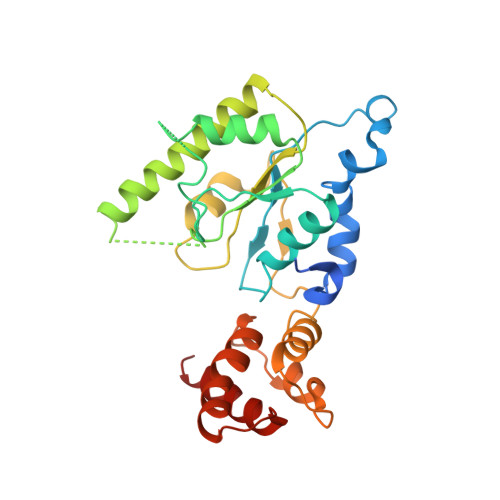
Conformational Landscape of the p28-Bound Human Proteasome Regulatory Particle.
Lu, Y., Wu, J., Dong, Y., Chen, S., Sun, S., Ma, Y.B., Ouyang, Q., Finley, D., Kirschner, M.W., Mao, Y.(2017) Mol Cell 67: 322-333.e6
- PubMed: 28689658
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VGZ, 5VHF, 5VHH, 5VHI, 5VHJ, 5VHM, 5VHN, 5VHO, 5VHP, 5VHQ, 5VHR, 5VHS - PubMed Abstract:
The proteasome holoenzyme is activated by its regulatory particle (RP) consisting of two subcomplexes, the lid and the base. A key event in base assembly is the formation of a heterohexameric ring of AAA-ATPases, which is guided by at least four RP assembly chaperones in mammals: PAAF1, p28/gankyrin, p27/PSMD9, and S5b. Using cryogenic electron microscopy, we analyzed the non-AAA structure of the p28-bound human RP at 4.5 Å resolution and determined seven distinct conformations of the Rpn1-p28-AAA subcomplex within the p28-bound RP at subnanometer resolutions. Remarkably, the p28-bound AAA ring does not form a channel in the free RP and spontaneously samples multiple "open" and "closed" topologies at the Rpt2-Rpt6 and Rpt3-Rpt4 interfaces. Our analysis suggests that p28 assists the proteolytic core particle to select a specific conformation of the ATPase ring for RP engagement and is released in a shoehorn-like fashion in the last step of the chaperone-mediated proteasome assembly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.