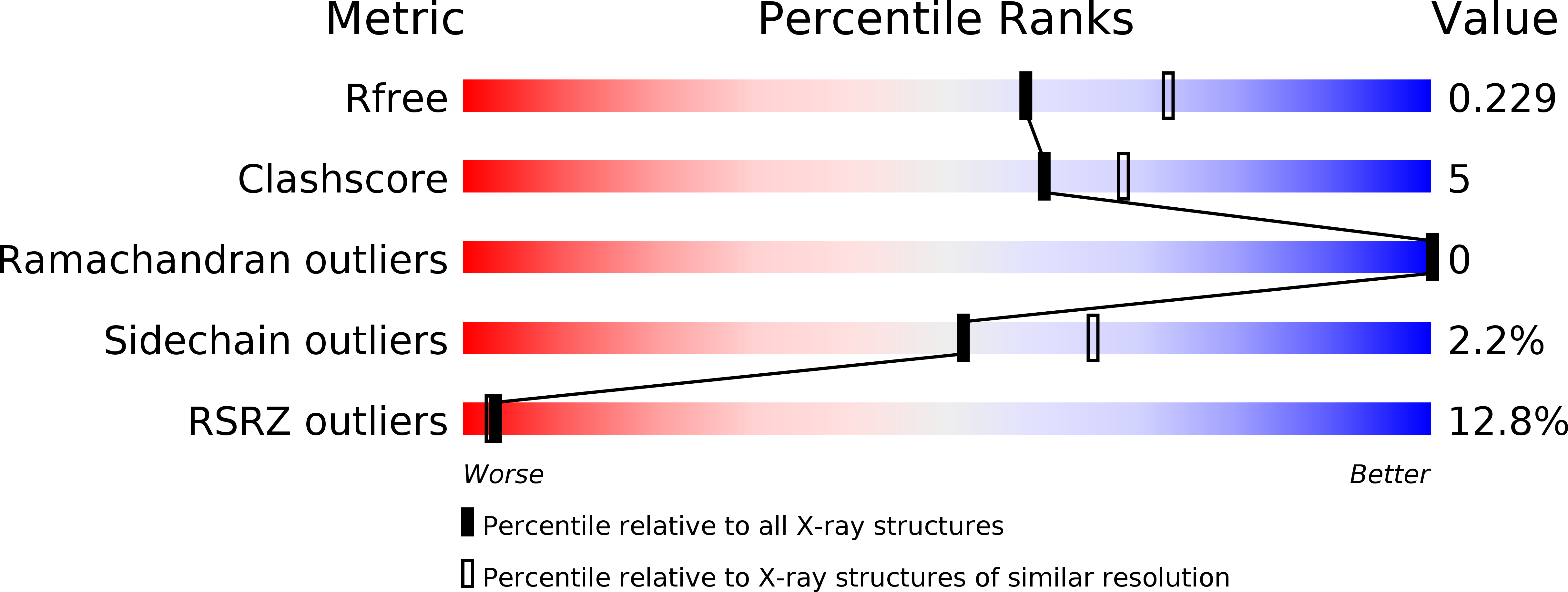
Azaindoles as Zinc-Binding Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the JAMM Protease CSN5.
Altmann, E., Erbel, P., Renatus, M., Schaefer, M., Schlierf, A., Druet, A., Kieffer, L., Sorge, M., Pfister, K., Hassiepen, U., Jones, M., Ruedisser, S., Ostermeier, D., Martoglio, B., Jefferson, A.B., Quancard, J.(2017) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56: 1294-1297
- PubMed: 27981705
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201608672
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5M5Q - PubMed Abstract:
CSN5 is the zinc metalloprotease subunit of the COP9 signalosome (CSN), which is an important regulator of cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases (CRLs). CSN5 is responsible for the cleavage of NEDD8 from CRLs, and blocking deconjugation of NEDD8 traps the CRLs in a hyperactive state, thereby leading to auto-ubiquitination and ultimately degradation of the substrate recognition subunits. Herein, we describe the discovery of azaindoles as a new class of CSN5 inhibitors, which interact with the active-site zinc ion of CSN5 through an unprecedented binding mode. The best compounds inhibited CSN5 with nanomolar potency, led to degradation of the substrate recognition subunit Skp2 in cells, and reduced the viability of HCT116 cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, Novartis Campus, 4002, Basel, Switzerland.