Novel (2,6-difluorophenyl)(2-(phenylamino)pyrimidin-4-yl)methanones with restricted conformation as potent non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors against HIV-1.
Simon, P., Baszczynski, O., Saman, D., Stepan, G., Hu, E., Lansdon, E.B., Jansa, P., Janeba, Z.(2016) Eur J Med Chem 122: 185-195
- PubMed: 27371922
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.06.026
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
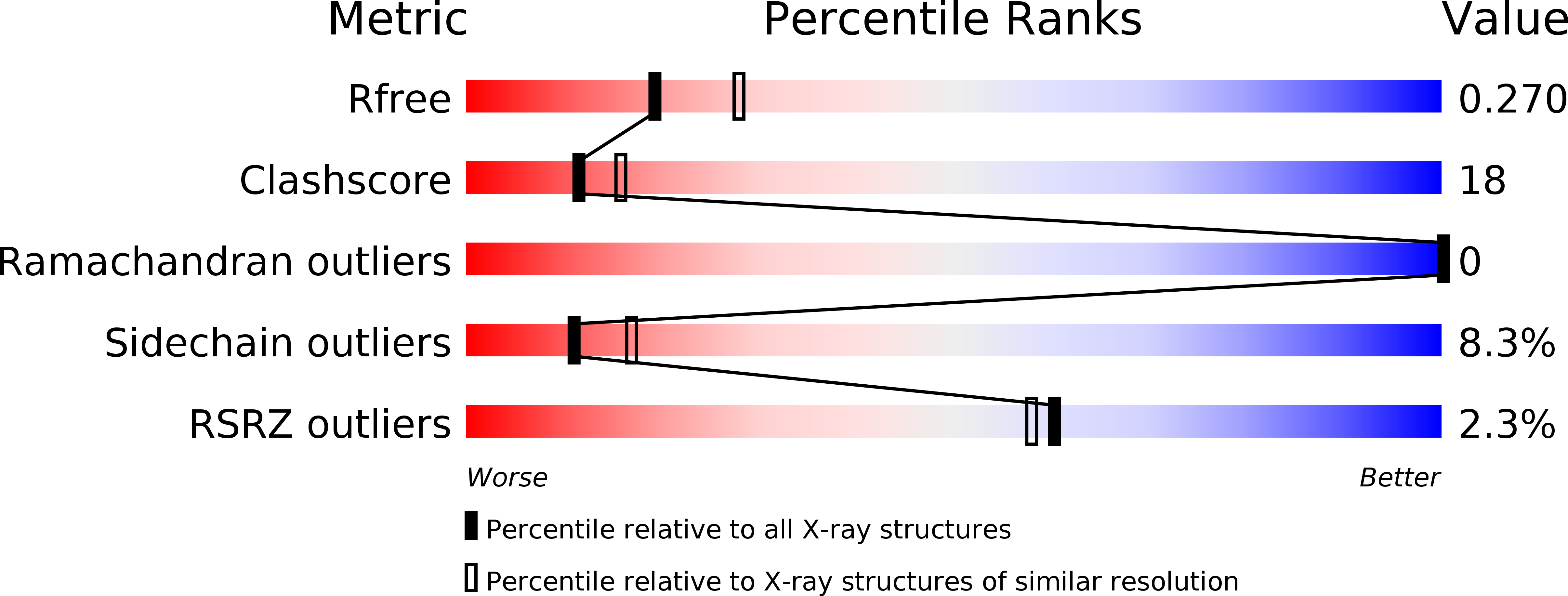
5K14 - PubMed Abstract:
To elucidate the structure-geometry-activity relationship in diarylpyrimidine family (DAPYs) containing carbonyl linker between the central pyrimidine core and phenyl type B-arm, a series of (2,6-difluorophenyl)(2-(phenylamino)pyrimidin-4-yl)methanones was designed, prepared and tested for their anti-HIV-1 activity. The carbonyl linker bearing B phenyl arm was successfully attached at both C-2 and C-4 positions of the central pyrimidine ring using a new synthetic approach. Further modifications of target compounds are present at C-5 position of the pyrimidine ring. In vitro anti-HIV-1 activity study performed on a series of 22 compounds confirmed the crucial importance of both conformational rigidity between phenyl B arm and the pyrimidine core linked through the carbonyl bridge, as well as presence of fluoro substituents in ortho-positions of phenyl B moiety. The most potent derivative of the series, compound 17, having almost perpendicular angle within the two planes made from the B aromatic arm and the pyrimidine ring, exhibited low nanomolar anti-HIV-1 activity (EC50 = 4 nM) with no significant toxicity (CC50 > 57.1 μM).
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, Czech Academy of Sciences, Flemingovo nám. 2, Prague-6 CZ-16610, Czech Republic.