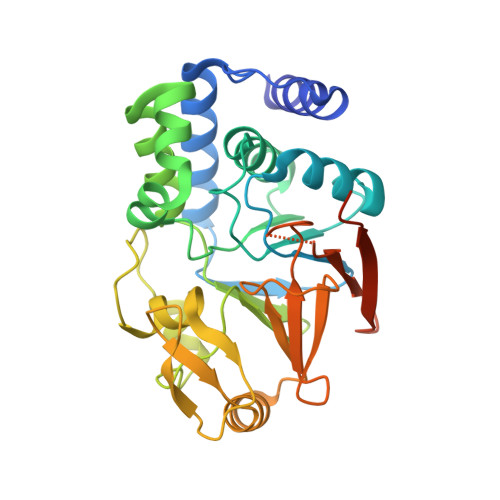
Molecular Insights into the Fungus-Specific Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatase Z1 in Candida albicans.
Chen, E., Choy, M.S., Petrenyi, K., Konya, Z., Erdodi, F., Dombradi, V., Peti, W., Page, R.(2016) mBio 7
- PubMed: 27578752
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00872-16
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JPE, 5JPF - PubMed Abstract:
The opportunistic pathogen Candida is one of the most common causes of nosocomial bloodstream infections. Because candidemia is associated with high mortality rates and because the incidences of multidrug-resistant Candida are increasing, efforts to identify novel targets for the development of potent antifungals are warranted. Here, we describe the structure and function of the first member of a family of protein phosphatases that is specific to fungi, protein phosphatase Z1 (PPZ1) from Candida albicans We show that PPZ1 not only is active but also is as susceptible to inhibition by the cyclic peptide inhibitor microcystin-LR as its most similar human homolog, protein phosphatase 1α (PP1α [GLC7 in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae]). Unexpectedly, we also discovered that, despite its 66% sequence identity to PP1α, the catalytic domain of PPZ1 contains novel structural elements that are not present in PP1α. We then used activity and pulldown assays to show that these structural differences block a large subset of PP1/GLC7 regulatory proteins from effectively binding PPZ1, demonstrating that PPZ1 does not compete with GLC7 for its regulatory proteins. Equally important, these unique structural elements provide new pockets suitable for the development of PPZ1-specific inhibitors. Together, these studies not only reveal why PPZ1 does not negatively impact GLC7 activity in vivo but also demonstrate that the family of fungus-specific phosphatases-especially PPZ1 from C. albicans-are highly suitable targets for the development of novel drugs that specifically target C. albicans without cross-reacting with human phosphatases. Candida albicans is a medically important human pathogen that is the most common cause of fungal infections in humans. In particular, approximately 46,000 cases of health care-associated candidiasis occur each year in the United States. Because these infections are associated with high mortality rates and because multiple species of Candida are becoming increasingly resistant to antifungals, there are increasing efforts to identify novel targets that are essential for C. albicans virulence. Here we use structural and biochemical approaches to elucidate how a member of a fungus-specific family of enzymes, serine/threonine phosphatase PPZ1, functions in C. albicans We discovered multiple unique features of PPZ1 that explain why it does not cross-react with, and in turn compete for, PP1-specific regulators, a long-standing question in the field. Most importantly, however, these unique features identified PPZ1 as a potential target for the development of novel antifungal therapeutics that will provide new, safe, and potent treatments for candidiasis in humans.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Cell Biology and Biochemistry, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island, USA.