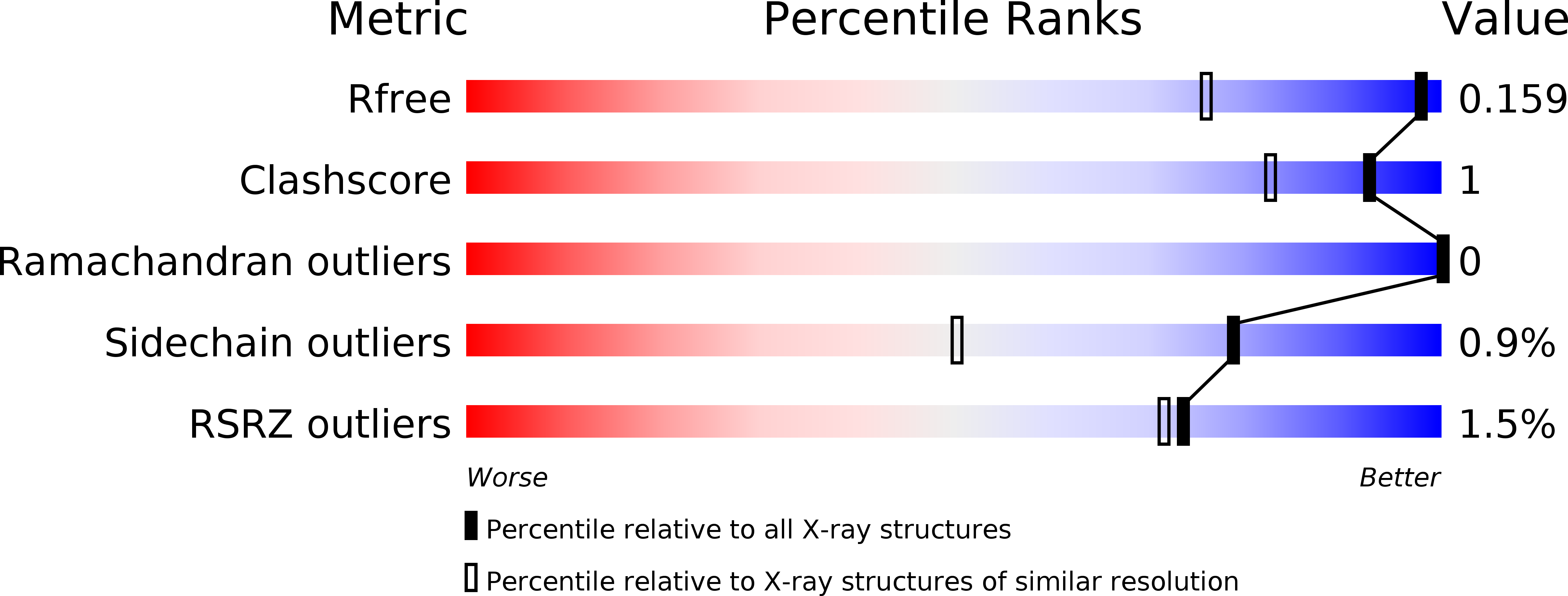
1.2 angstrom resolution crystal structure of the periplasmic aminotransferase PvdN from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Drake, E.J., Gulick, A.M.(2016) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 72: 403-408
- PubMed: 27139833
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X16006257
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5I90 - PubMed Abstract:
The Gram-negative pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) biosynthetic cluster for the production of a peptide siderophore. In addition to four multimodular NRPS proteins, the biosynthetic pathway also requires several additional enzymes involved in the production of nonproteinogenic amino acids and maturation of the peptide product. Among the proteins that are required for the final steps in pyoverdine synthesis is PvdN, a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme that catalyzes an uncharacterized step in pyoverdine production. This study reports the high-resolution structure of PvdN bound to a PLP cofactor solved by multi-wavelength anomalous dispersion (MAD). The PvdN model shows high structural homology to type I aspartate aminotransferases and also contains positive density that suggests an uncharacterized external aldimine.
Organizational Affiliation:
Hauptman-Woodward Institute, 700 Ellicott Street, Buffalo, NY 14203, USA.