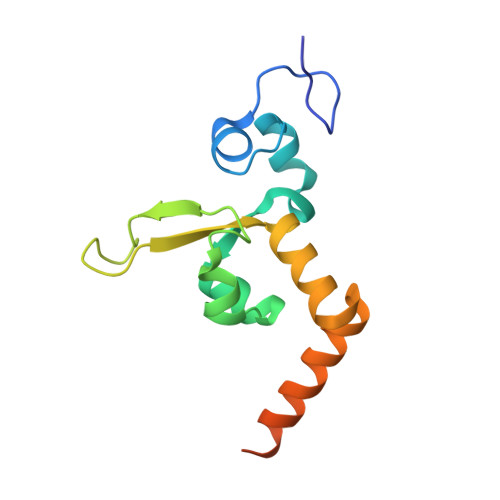
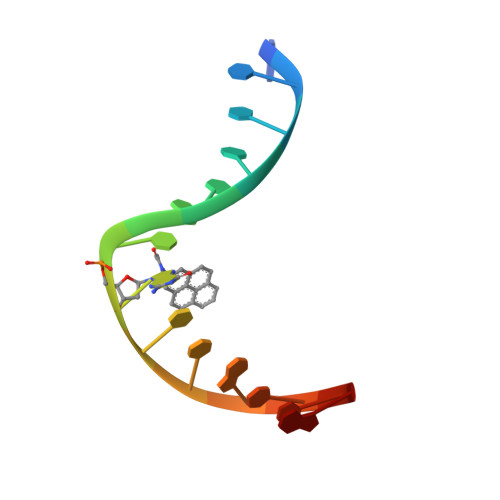
Structural Basis for Bulky Adduct DNA Lesion Recognition by the Nucleotide Excision Repair Protein Rad14.
Schneider, S., Simon, N., Ebert, C.(2016) Chemistry 22: 10782
- PubMed: 27223336
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201602438
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5G32, 5G33, 5G34, 5G35 - PubMed Abstract:
Heterocyclic aromatic amines react with purine bases and result in bulky DNA adducts that cause mutations. Such structurally diverse lesions are substrates for the nucleotide excision repair (NER). It is thought that the NER machinery recognises and verifies distorted DNA conformations, also involving the xeroderma pigmentosum group A and C proteins (XPA, XPC) that act as a scaffold between the DNA substrate and several other NER proteins. Here we present the synthesis of DNA molecules containing the polycyclic, aromatic amine C8-guanine lesions acetylaminophenyl, acetylaminonaphthyl, acetylaminoanthryl, and acetylaminopyrenyl, as well as their crystal structures in complex with the yeast XPA homologue Rad14. This work further substantiates the indirect lesion-detection mechanism employed by the NER system that recognises destabilised and deformable DNA structures.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich CIPSM, Department of Chemistry, Ludwig-Maximilians Universität München, Butenandtstrasse 13, 81377, München, Germany.