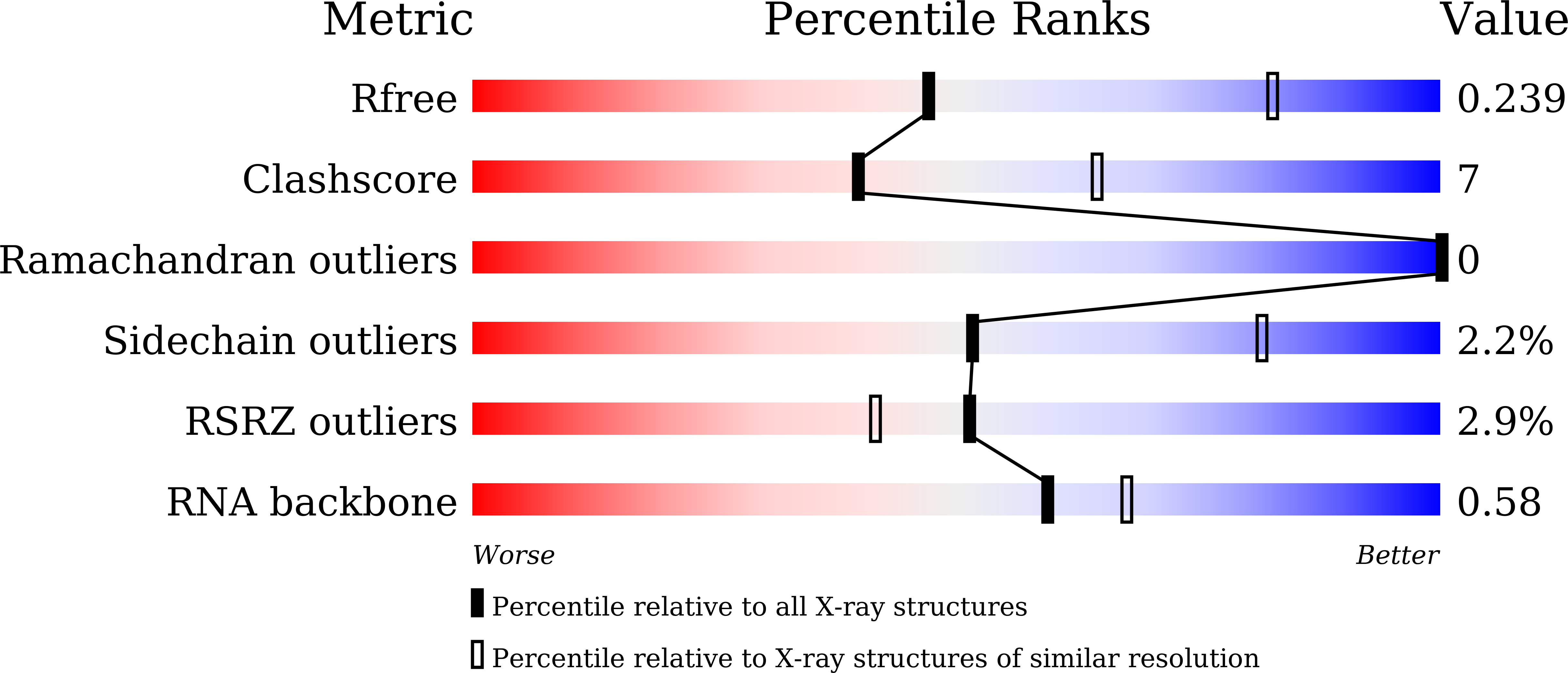
Structural basis of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalysis and translocation
Shu, B., Gong, P.(2016) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113: E4005-E4014
- PubMed: 27339134
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1602591113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5F8G, 5F8H, 5F8I, 5F8J, 5F8L, 5F8M, 5F8N - PubMed Abstract:
Viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRPs) play essential roles in viral genome replication and transcription. We previously reported several structural states of the poliovirus RdRP nucleotide addition cycle (NAC) that revealed a unique palm domain-based active site closure mechanism and proposed a six-state NAC model including a hypothetical state representing translocation intermediates. Using the RdRP from another human enterovirus, enterovirus 71, here we report seven RdRP elongation complex structures derived from a crystal lattice that allows three NAC events. These structures suggested a key order of events in initial NTP binding and NTP-induced active site closure and revealed a bona fide translocation intermediate featuring asymmetric movement of the template-product duplex. Our work provides essential missing links in understanding NTP recognition and translocation mechanisms in viral RdRPs and emphasizes the uniqueness of the viral RdRPs compared with other processive polymerases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, Hubei 430071, China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.