Small Molecule Inhibitors of Ca(2+)-S100B Reveal Two Protein Conformations.
Cavalier, M.C., Ansari, M.I., Pierce, A.D., Wilder, P.T., McKnight, L.E., Raman, E.P., Neau, D.B., Bezawada, P., Alasady, M.J., Charpentier, T.H., Varney, K.M., Toth, E.A., MacKerell, A.D., Coop, A., Weber, D.J.(2016) J Med Chem 59: 592-608
- PubMed: 26727270
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01369
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
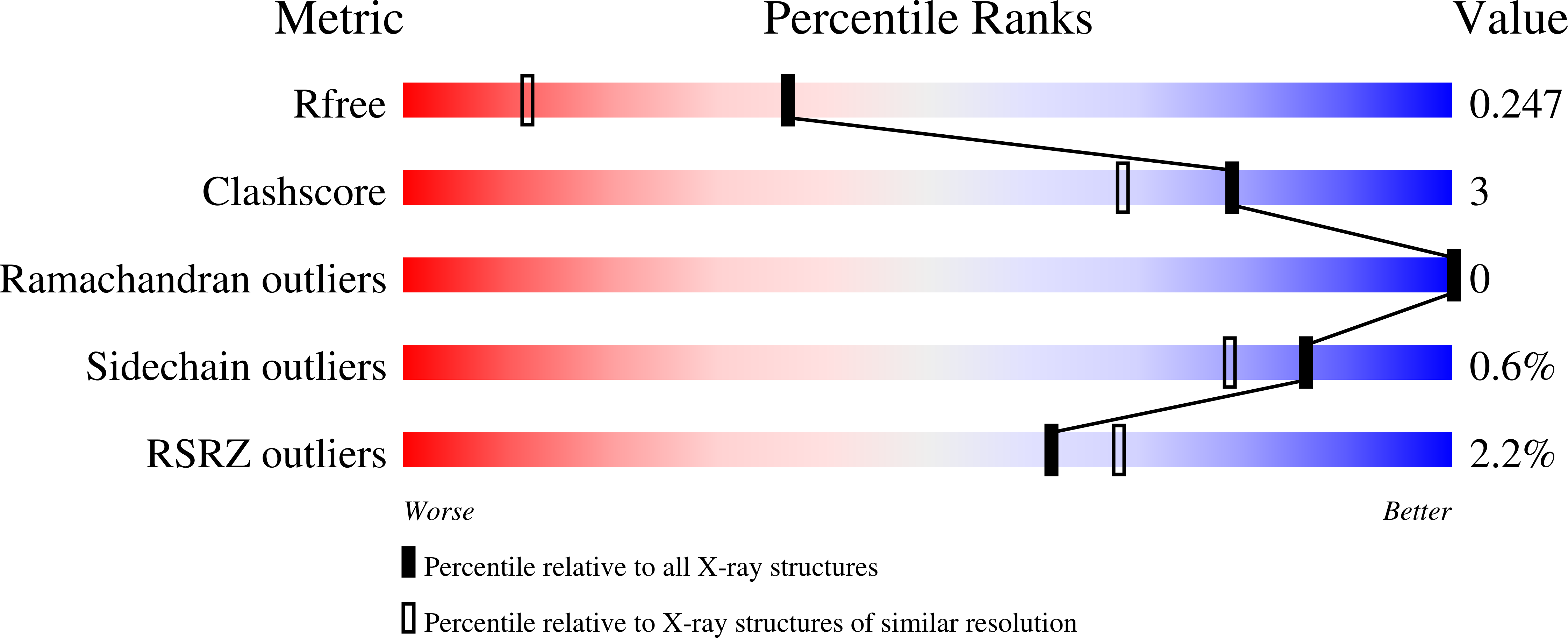
5DKN, 5DKQ, 5DKR - PubMed Abstract:
The drug pentamidine inhibits calcium-dependent complex formation with p53 ((Ca)S100B·p53) in malignant melanoma (MM) and restores p53 tumor suppressor activity in vivo. However, off-target effects associated with this drug were problematic in MM patients. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies were therefore completed here with 23 pentamidine analogues, and X-ray structures of (Ca)S100B·inhibitor complexes revealed that the C-terminus of S100B adopts two different conformations, with location of Phe87 and Phe88 being the distinguishing feature and termed the "FF-gate". For symmetric pentamidine analogues ((Ca)S100B·5a, (Ca)S100B·6b) a channel between sites 1 and 2 on S100B was occluded by residue Phe88, but for an asymmetric pentamidine analogue ((Ca)S100B·17), this same channel was open. The (Ca)S100B·17 structure illustrates, for the first time, a pentamidine analog capable of binding the "open" form of the "FF-gate" and provides a means to block all three "hot spots" on (Ca)S100B, which will impact next generation (Ca)S100B·p53 inhibitor design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Center for Biomolecular Therapeutics (CBT), University of Maryland School of Medicine , Baltimore, Maryland 21201, United States.