Structure and Engineering of Francisella novicida Cas9
Hirano, H., Gootenberg, J.S., Horii, T., Abudayyeh, O.O., Kimura, M., Hsu, P.D., Nakane, T., Ishitani, R., Hatada, I., Zhang, F., Nishimasu, H., Nureki, O.(2016) Cell 164: 950-961
- PubMed: 26875867
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.039
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
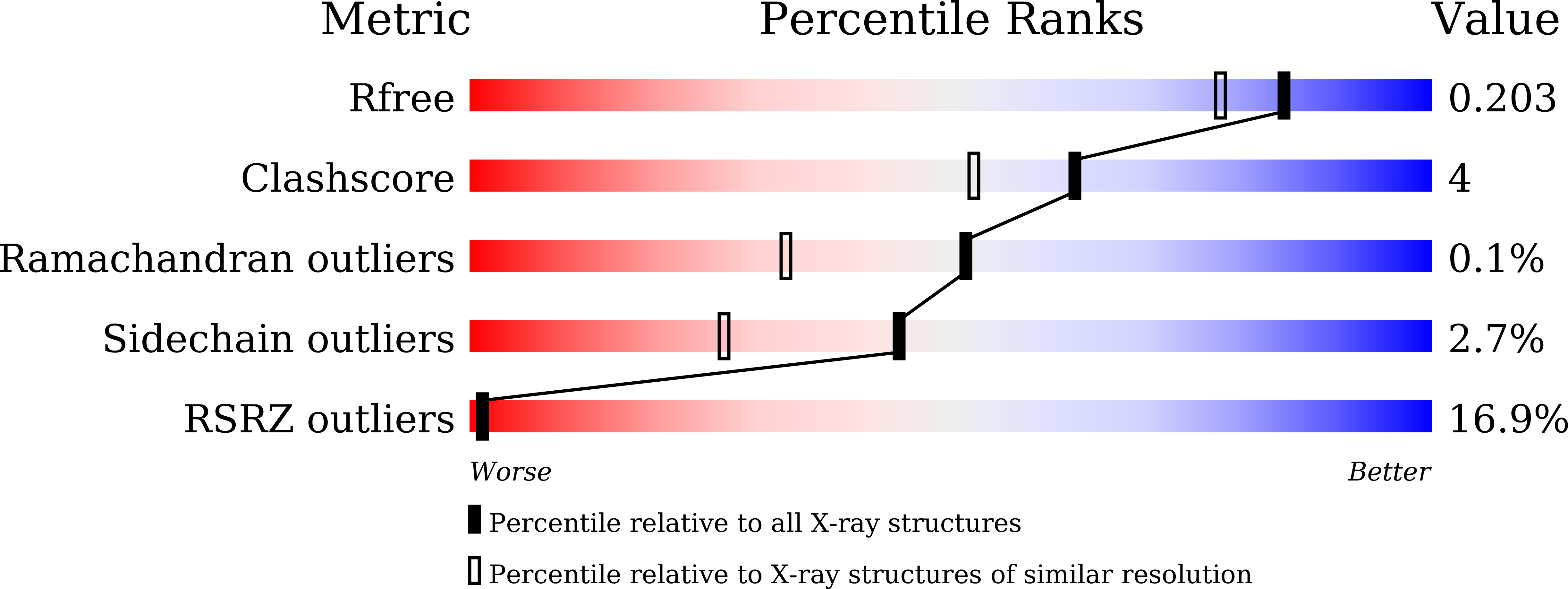
5B2O, 5B2P, 5B2Q - PubMed Abstract:
The RNA-guided endonuclease Cas9 cleaves double-stranded DNA targets complementary to the guide RNA and has been applied to programmable genome editing. Cas9-mediated cleavage requires a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) juxtaposed with the DNA target sequence, thus constricting the range of targetable sites. Here, we report the 1.7 Å resolution crystal structures of Cas9 from Francisella novicida (FnCas9), one of the largest Cas9 orthologs, in complex with a guide RNA and its PAM-containing DNA targets. A structural comparison of FnCas9 with other Cas9 orthologs revealed striking conserved and divergent features among distantly related CRISPR-Cas9 systems. We found that FnCas9 recognizes the 5'-NGG-3' PAM, and used the structural information to create a variant that can recognize the more relaxed 5'-YG-3' PAM. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the FnCas9-ribonucleoprotein complex can be microinjected into mouse zygotes to edit endogenous sites with the 5'-YG-3' PAM, thus expanding the target space of the CRISPR-Cas9 toolbox.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, 2-11-16 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0032, Japan.