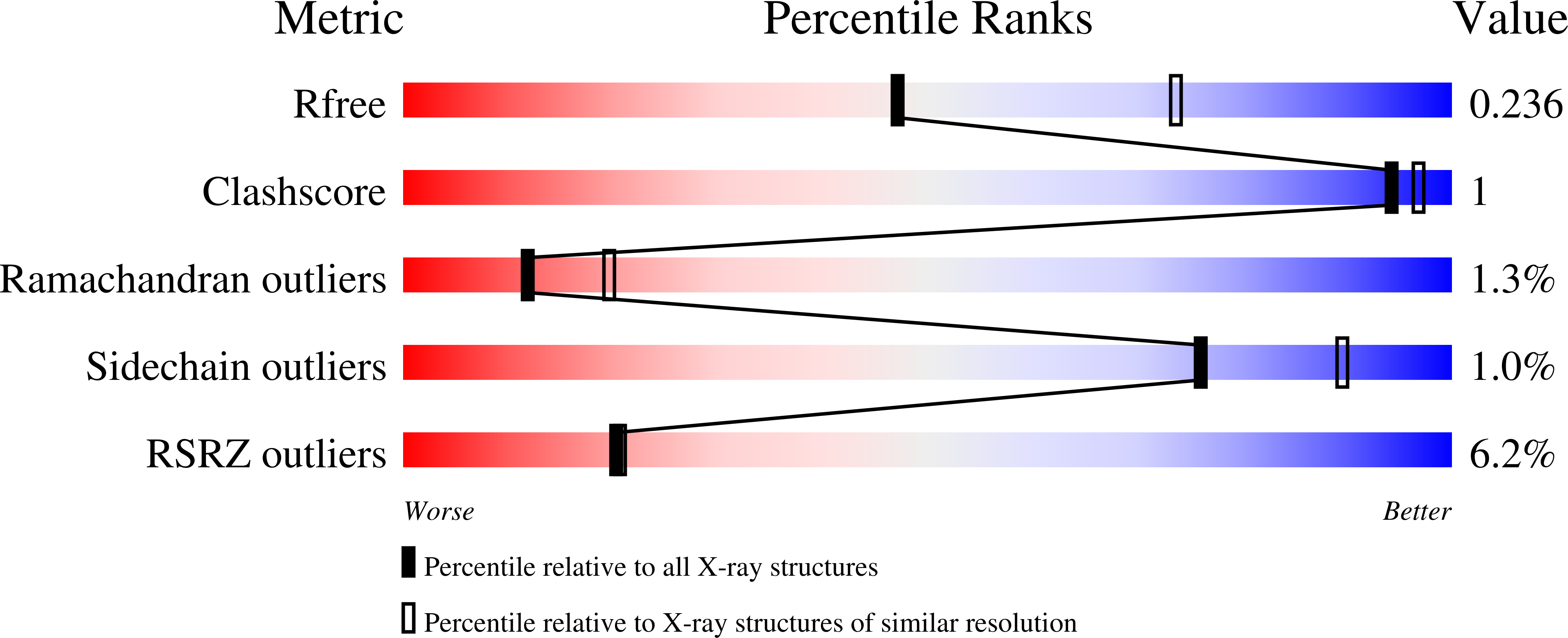
Structure of the Francisella response regulator QseB receiver domain, and characterization of QseB inhibition by antibiofilm 2-aminoimidazole-based compounds.
Milton, M.E., Allen, C.L., Feldmann, E.A., Bobay, B.G., Jung, D.K., Stephens, M.D., Melander, R.J., Theisen, K.E., Zeng, D., Thompson, R.J., Melander, C., Cavanagh, J.(2017) Mol Microbiol 106: 223-235
- PubMed: 28755524
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13759
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UIC - PubMed Abstract:
With antibiotic resistance increasing at alarming rates, targets for new antimicrobial therapies must be identified. A particularly promising target is the bacterial two-component system. Two-component systems allow bacteria to detect, evaluate and protect themselves against changes in the environment, such as exposure to antibiotics and also to trigger production of virulence factors. Drugs that target the response regulator portion of two-component systems represent a potent new approach so far unexploited. Here, we focus efforts on the highly virulent bacterium Francisella tularensis tularensis. Francisella contains only three response regulators, making it an ideal system to study. In this study, we initially present the structure of the N-terminal domain of QseB, the response regulator responsible for biofilm formation. Subsequently, using binding assays, computational docking and cellular studies, we show that QseB interacts with2-aminoimidazole based compounds that impede its function. This information will assist in tailoring compounds to act as adjuvants that will enhance the effect of antibiotics.
Organizational Affiliation:
RTI International, 3040 Cornwallis Rd, RTP, NC 27709, USA.