Molecular architecture and dynamics of ASH1 mRNA recognition by its mRNA-transport complex.
Edelmann, F.T., Schlundt, A., Heym, R.G., Jenner, A., Niedner-Boblenz, A., Syed, M.I., Paillart, J.C., Stehle, R., Janowski, R., Sattler, M., Jansen, R.P., Niessing, D.(2017) Nat Struct Mol Biol 24: 152-161
- PubMed: 28092367
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3351
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5M0H, 5M0I, 5M0J - PubMed Abstract:
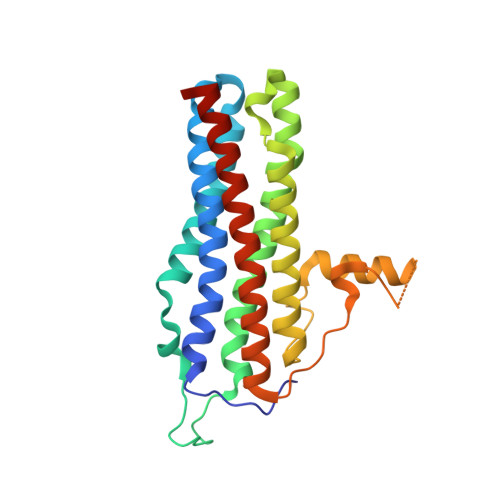
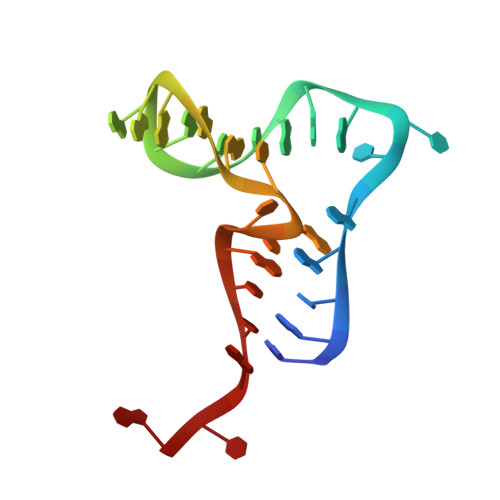
mRNA localization is an essential mechanism of gene regulation and is required for processes such as stem-cell division, embryogenesis and neuronal plasticity. It is not known which features in the cis-acting mRNA localization elements (LEs) are specifically recognized by motor-containing transport complexes. To the best of our knowledge, no high-resolution structure is available for any LE in complex with its cognate protein complex. Using X-ray crystallography and complementary techniques, we carried out a detailed assessment of an LE of the ASH1 mRNA from yeast, its complex with its shuttling RNA-binding protein She2p, and its highly specific, cytoplasmic complex with She3p. Although the RNA alone formed a flexible stem loop, She2p binding induced marked conformational changes. However, only joining by the unstructured She3p resulted in specific RNA recognition. The notable RNA rearrangements and joint action of a globular and an unfolded RNA-binding protein offer unprecedented insights into the step-wise maturation of an mRNA-transport complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Structural Biology, Helmholtz Zentrum München - German Research Center for Environmental Health, Neuherberg, Germany.