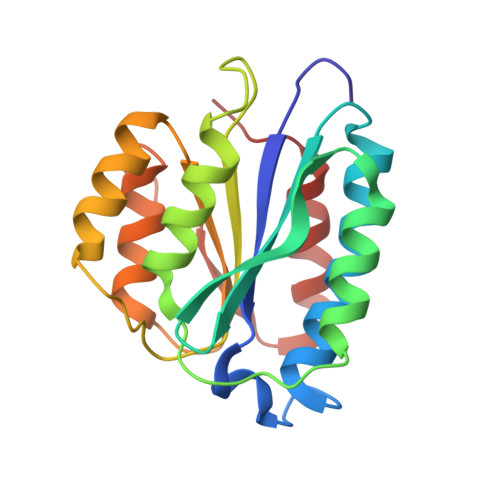
Crystal structure of the Rad3/XPD regulatory domain of Ssl1/p44
Kim, J.S., Saint-Andre, C., Lim, H.S., Hwang, C.S., Egly, J.M., Cho, Y.(2015) J Biol Chem 290: 8321-8330
- PubMed: 25681444
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.636514
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WFQ - PubMed Abstract:
The Ssl1/p44 subunit is a core component of the yeast/mammalian general transcription factor TFIIH, which is involved in transcription and DNA repair. Ssl1/p44 binds to and stimulates the Rad3/XPD helicase activity of TFIIH. To understand the helicase stimulatory mechanism of Ssl1/p44, we determined the crystal structure of the N-terminal regulatory domain of Ssl1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Ssl1 forms a von Willebrand factor A fold in which a central six-stranded β-sheet is sandwiched between three α helices on both sides. Structural and biochemical analyses of Ssl1/p44 revealed that the β4-α5 loop, which is frequently found at the interface between von Willebrand factor A family proteins and cellular counterparts, is critical for the stimulation of Rad3/XPD. Yeast genetics analyses showed that double mutation of Leu-239 and Ser-240 in the β4-α5 loop of Ssl1 leads to lethality of a yeast strain, demonstrating the importance of the Rad3-Ssl1 interactions to cell viability. Here, we provide a structural model for the Rad3/XPD-Ssl1/p44 complex and insights into how the binding of Ssl1/p44 contributes to the helicase activity of Rad3/XPD and cell viability.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Life Science, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang 790-784, South Korea and.