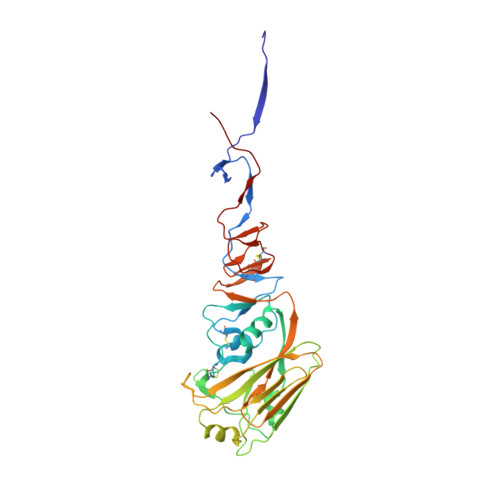
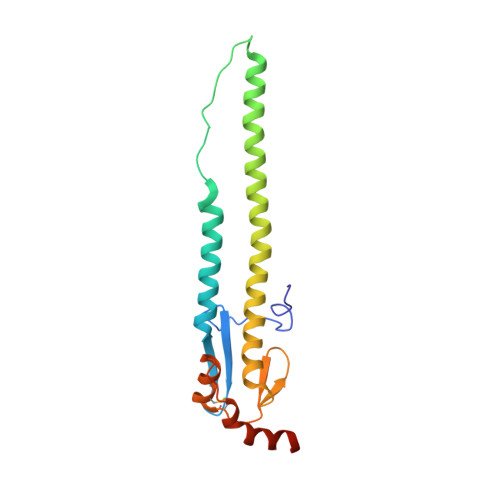
Alternative Recognition of the Conserved Stem Epitope in Influenza A Virus Hemagglutinin by a VH3-30-Encoded Heterosubtypic Antibody.
Wyrzucki, A., Dreyfus, C., Kohler, I., Steck, M., Wilson, I.A., Hangartner, L.(2014) J Virol 88: 7083-7092
- PubMed: 24719426
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00178-14
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PY7, 4PY8 - PubMed Abstract:
A human monoclonal heterosubtypic antibody, MAb 3.1, with its heavy chain encoded by VH3-30, was isolated using phage display with immobilized hemagglutinin (HA) from influenza virus A/Japan/305/1957(H2N2) as the target. Antibody 3.1 potently neutralizes influenza viruses from the H1a clade (i.e., H1, H2, H5, H6) but has little neutralizing activity against the H1b clade. Its crystal structure in complex with HA from a pandemic H1N1 influenza virus, A/South Carolina/1/1918(H1N1), revealed that like other heterosubtypic anti-influenza virus antibodies, MAb 3.1 contacts a hydrophobic groove in the HA stem, primarily using its heavy chain. However, in contrast to the closely related monoclonal antibody (Mab) FI6 that relies heavily on HCDR3 for binding, MAb 3.1 utilizes residues from HCDR1, HCDR3, and framework region 3 (FR3). Interestingly, HCDR1 of MAb 3.1 adopts an α-helical conformation and engages in hydrophobic interactions with the HA very similar to those of the de novo in silico-designed and affinity-matured synthetic protein HB36.3. These findings improve our understanding of the molecular requirements for binding to the conserved epitope in the stem of the HA protein and, therefore, aid the development of more universal influenza vaccines targeting these epitopes. Influenza viruses rapidly evade preexisting immunity by constantly altering the immunodominant neutralizing antibody epitopes (antigenic drift) or by acquiring new envelope serotypes (antigenic shift). As a consequence, the majority of antibodies elicited by immunization or infection protect only against the immunizing or closely related strains. Here, we describe a novel monoclonal antibody that recognizes the conserved heterosubtypic epitope in the stem of influenza A virus hemagglutinin. This antibody, referred to as MAb 3.1, recognizes its epitope in a manner that resembles recognition of a similar epitope by the de novo in silico-designed and affinity-matured synthetic protein HB36.3. Thus, besides providing novel insights into the molecular interactions between heterosubtypic antibodies and influenza virus hemagglutinin, MAb 3.1 demonstrates that de novo in silico-designed and affinity-matured synthetic proteins can foretell naturally selected antibody binding. This knowledge will aid development of a pan-influenza virus vaccine.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Medical Virology, University of Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland.