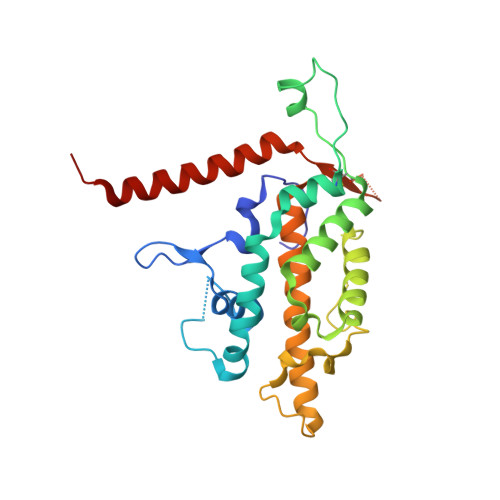
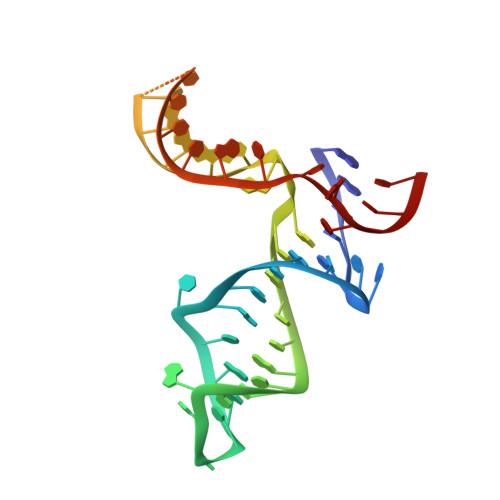
Structural basis for protein-RNA recognition in telomerase.
Huang, J., Brown, A.F., Wu, J., Xue, J., Bley, C.J., Rand, D.P., Wu, L., Zhang, R., Chen, J.J., Lei, M.(2014) Nat Struct Mol Biol 21: 507-512
- PubMed: 24793650
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2819
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4O26 - PubMed Abstract:
Telomerase is a large ribonucleoprotein complex minimally composed of a catalytic telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) and an RNA component (TR) that provides the template for telomeric DNA synthesis. However, it remains unclear how TERT and TR assemble into a functional telomerase. Here we report the crystal structure of the conserved regions 4 and 5 (CR4/5) of TR in complex with the TR-binding domain (TRBD) of TERT from the teleost fish Oryzias latipes. The structure shows that CR4/5 adopts an L-shaped three-way-junction conformation with its two arms clamping onto TRBD. Both the sequence and conformation of CR4/5 are required for the interaction. Our structural and mutational analyses suggest that the observed CR4/5-TRBD recognition is common to most eukaryotes, and CR4/5 in vertebrate TR might have a similar role in telomerase regulation as that of stem-loop IV in Tetrahymena TR.
Organizational Affiliation:
1] National Center for Protein Science Shanghai, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China. [2] Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA. [3] Department of Biological Chemistry, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA.