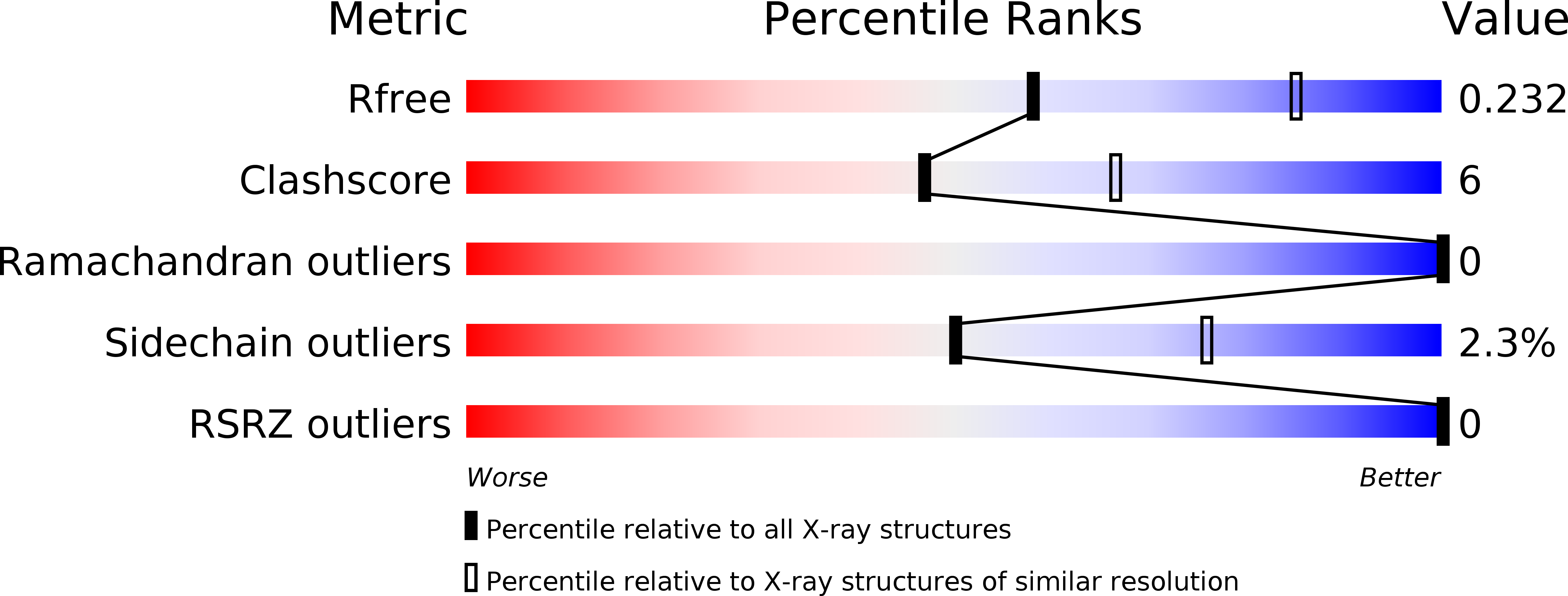
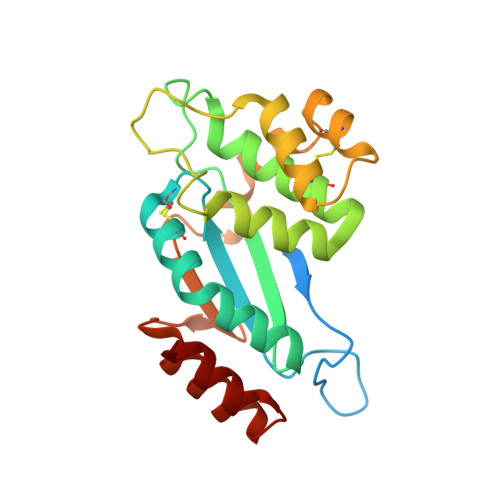
Structure analysis of the extracellular domain reveals disulfide bond forming-protein properties of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2969c.
Wang, L., Li, J., Wang, X., Liu, W., Zhang, X.C., Li, X., Rao, Z.(2013) Protein Cell 4: 628-640
- PubMed: 23828196
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-013-3033-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JR4, 4JR6 - PubMed Abstract:
Disulfide bond-forming (Dsb) protein is a bacterial periplasmic protein that is essential for the correct folding and disulfide bond formation of secreted or cell wallassociated proteins. DsbA introduces disulfide bonds into folding proteins, and is re-oxidized through interaction with its redox partner DsbB. Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a Gram-positive bacterium, expresses a DsbA-like protein ( Rv2969c), an extracellular protein that has its Nterminus anchored in the cell membrane. Since Rv2969c is an essential gene, crucial for disulfide bond formation, research of DsbA may provide a target of a new class of anti-bacterial drugs for treatment of M.tuberculosis infection. In the present work, the crystal structures of the extracellular region of Rv2969c (Mtb DsbA) were determined in both its reduced and oxidized states. The overall structure of Mtb DsbA can be divided into two domains: a classical thioredoxin-like domain with a typical CXXC active site, and an α-helical domain. It largely resembles its Escherichia coli homologue EcDsbA, however, it possesses a truncated binding groove; in addition, its active site is surrounded by an acidic, rather than hydrophobic surface. In our oxidoreductase activity assay, Mtb DsbA exhibited a different substrate specificity when compared to EcDsbA. Moreover, structural analysis revealed a second disulfide bond in Mtb DsbA, which is rare in the previously reported DsbA structures, and is assumed to contribute to the overall stability of Mtb DsbA. To investigate the disulphide formation pathway in M.tuberculosis, we modeled Mtb Vitamin K epoxide reductase (Mtb VKOR), a binding partner of Mtb DsbA, to Mtb DsbA.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.