PLP undergoes conformational changes during the course of an enzymatic reaction.
Ngo, H.P., Cerqueira, N.M., Kim, J.K., Hong, M.K., Fernandes, P.A., Ramos, M.J., Kang, L.W.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 596-606
- PubMed: 24531493
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004713031283
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
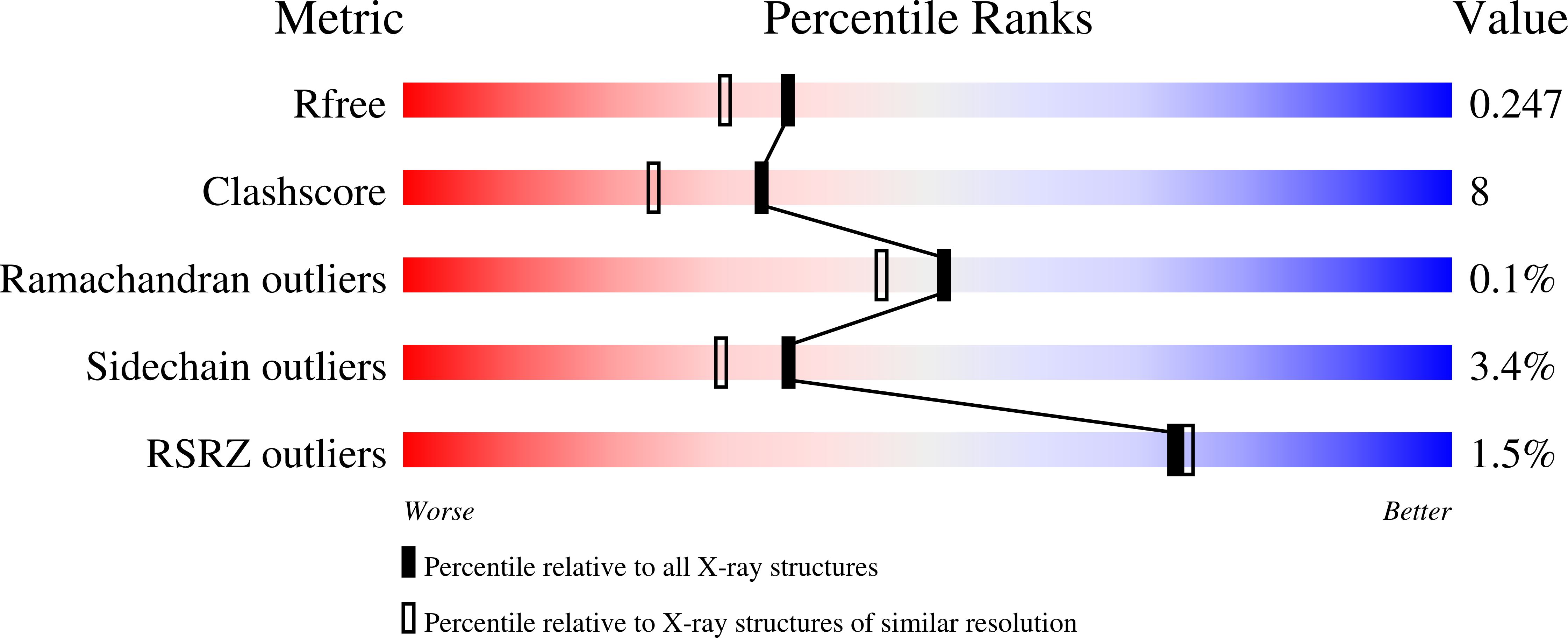
4IXS, 4IXZ, 4IY7, 4IYO - PubMed Abstract:
Numerous enzymes, such as the pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)-dependent enzymes, require cofactors for their activities. Using X-ray crystallography, structural snapshots of the L-serine dehydratase catalytic reaction of a bacterial PLP-dependent enzyme were determined. In the structures, the dihedral angle between the pyridine ring and the Schiff-base linkage of PLP varied from 18° to 52°. It is proposed that the organic cofactor PLP directly catalyzes reactions by active conformational changes, and the novel catalytic mechanism involving the PLP cofactor was confirmed by high-level quantum-mechanical calculations. The conformational change was essential for nucleophilic attack of the substrate on PLP, for concerted proton transfer from the substrate to the protein and for directing carbanion formation of the substrate. Over the whole catalytic cycle, the organic cofactor catalyzes a series of reactions, like the enzyme. The conformational change of the PLP cofactor in catalysis serves as a starting point for identifying the previously unknown catalytic roles of organic cofactors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Konkuk University, 1 Hwayang dong, Gwangjin-gu, Seoul 143-701, Republic of Korea.