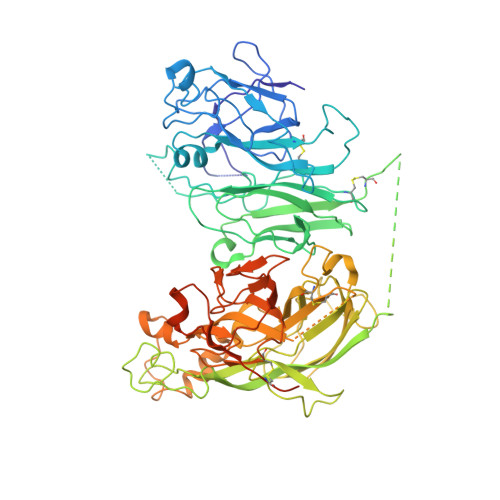
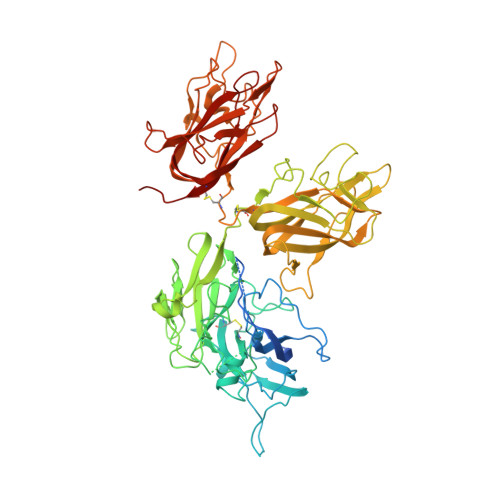
Evaluation of the Metal Binding Sites in a Recombinant Coagulation Factor Viii Identifies Two Sites with Unique Metal Binding Properties.
Svensson, L.A., Thim, L., Olsen, O.H., Nicolaisen, E.M.(2013) Biol Chem 394: 761
- PubMed: 23435097
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2012-0298
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BDV - PubMed Abstract:
Coagulation factor VIII is a glycosylated, non-covalent heterodimer consisting of a heavy chain (A1-A2-B domains) and a light chain (A3-C1-C2 domains). The association of the chains, and the stability and function of the dimer depend on the presence of metal ions. We applied X-ray fluorescence, X-ray crystallographic structure determination with anomalous signals at different wavelengths, and colorimetric measurements to evaluate the metal binding sites in a recombinant factor VIII molecule, turoctocog alfa. We identified a metal binding site in domain A3 dominated by Cu(+) binding and a site in domain A1 dominated by Zn(2+) binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
Novo Nordisk A/S, Novo Nordisk Park, DK-2760 Måløv, Denmark. AnSv@novonordisk.com