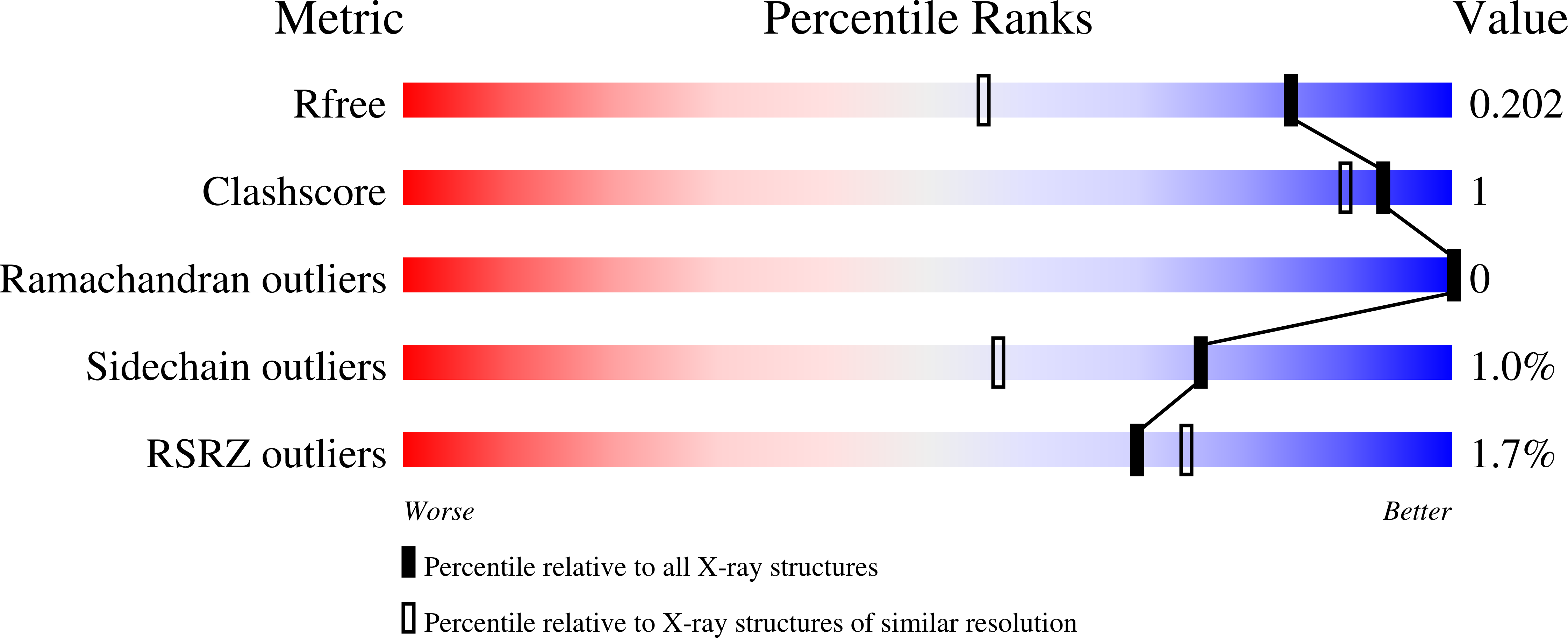
Crystal structures of the Helicobacter pylori MTAN enzyme reveal specific interactions between S-adenosylhomocysteine and the 5'-alkylthio binding subsite.
Mishra, V., Ronning, D.R.(2012) Biochemistry 51: 9763-9772
- PubMed: 23148563
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi301221k
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4OJT, 4OY3, 4P54 - PubMed Abstract:
The bacterial 5'-methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase (MTAN) enzyme is a multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the N-ribosidic bond of at least four different adenosine-based metabolites: S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH), 5'-methylthioadenosine (MTA), 5'-deoxyadenosine (5'-DOA), and 6-amino-6-deoxyfutalosine. These activities place the enzyme at the hub of seven fundamental bacterial metabolic pathways: S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) utilization, polyamine biosynthesis, the purine salvage pathway, the methionine salvage pathway, the SAM radical pathways, autoinducer-2 biosynthesis, and menaquinone biosynthesis. The last pathway makes MTAN essential for Helicobacter pylori viability. Although structures of various bacterial and plant MTANs have been described, the interactions between the homocysteine moiety of SAH and the 5'-alkylthiol binding site of MTAN have never been resolved. We have determined crystal structures of an inactive mutant form of H. pylori MTAN bound to MTA and SAH to 1.63 and 1.20 Å, respectively. The active form of MTAN was also crystallized in the presence of SAH, allowing the determination of the structure of a ternary enzyme-product complex resolved at 1.50 Å. These structures identify interactions between the homocysteine moiety and the 5'-alkylthiol binding site of the enzyme. This information can be leveraged for the development of species-specific MTAN inhibitors that prevent the growth of H. pylori.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Toledo, Toledo, OH 43606, USA.