Crystal Structures of Two Bacillus Carboxylesterases with Different Enantioselectivities.
Rozeboom, H.J., Godinho, L.F., Nardini, M., Quax, W.J., Dijkstra, B.W.(2014) Biochim Biophys Acta 1844: 567
- PubMed: 24418394
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.01.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4CCW, 4CCY - PubMed Abstract:
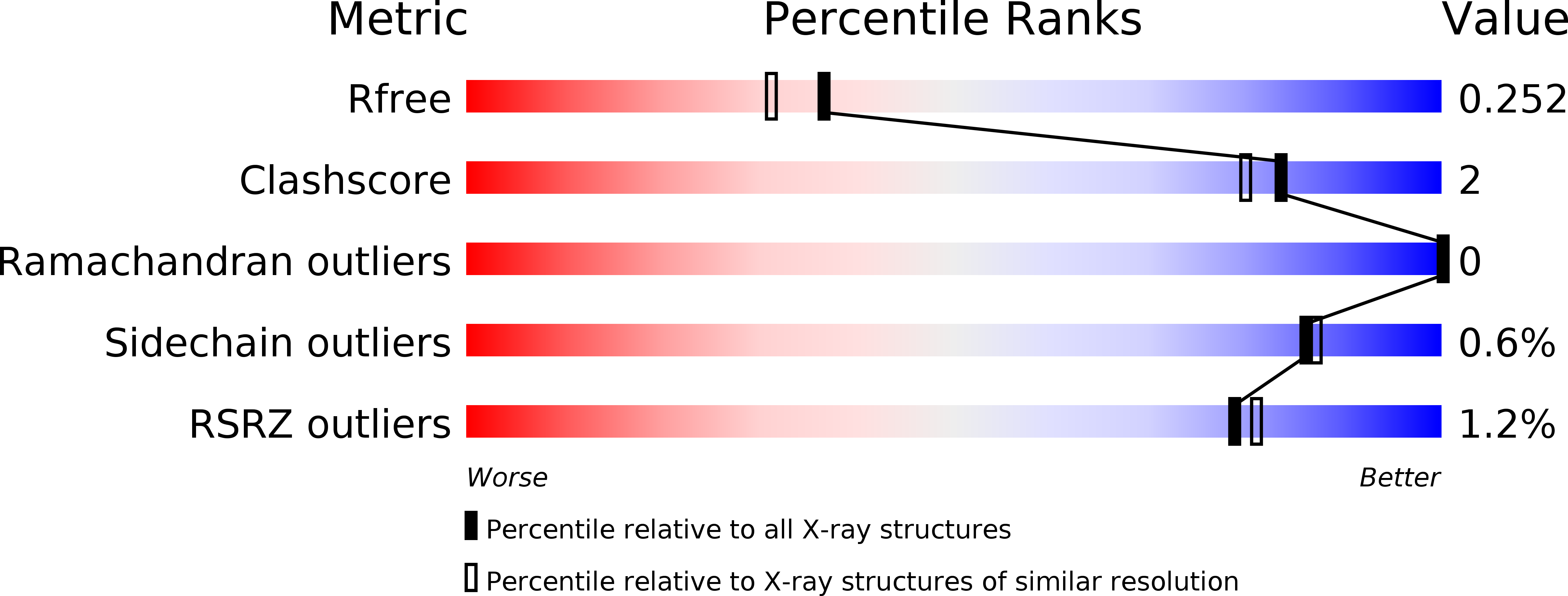
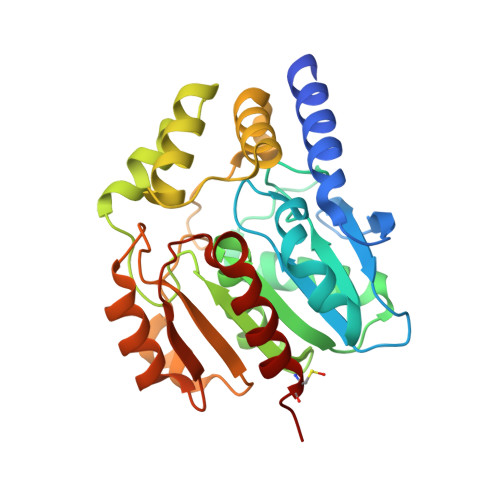
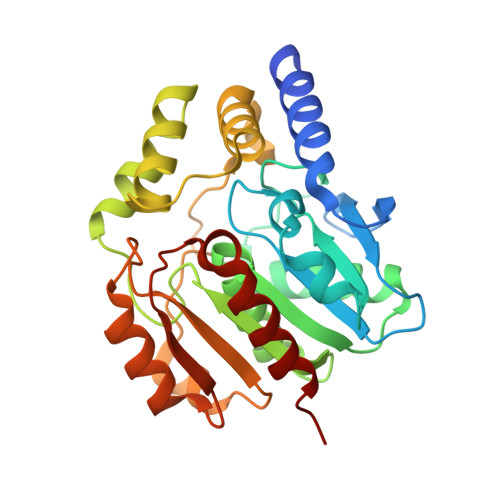
Naproxen esterase (NP) from Bacillus subtilis Thai I-8 is a carboxylesterase that catalyzes the enantioselective hydrolysis of naproxenmethylester to produce S-naproxen (E>200). It is a homolog of CesA (98% sequence identity) and CesB (64% identity), both produced by B. subtilis strain 168. CesB can be used for the enantioselective hydrolysis of 1,2-O-isopropylideneglycerol (solketal) esters (E>200 for IPG-caprylate). Crystal structures of NP and CesB, determined to a resolution of 1.75Å and 2.04Å, respectively, showed that both proteins have a canonical α/β hydrolase fold with an extra N-terminal helix stabilizing the cap subdomain. The active site in both enzymes is located in a deep hydrophobic groove and includes the catalytic triad residues Ser130, His274, and Glu245. A product analog, presumably 2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)acetic acid, was bound in the NP active site. The enzymes have different enantioselectivities, which previously were shown to result from only a few amino acid substitutions in the cap domain. Modeling of a substrate in the active site of NP allowed explaining the different enantioselectivities. In addition, Ala156 may be a determinant of enantioselectivity as well, since its side chain appears to interfere with the binding of certain R-enantiomers in the active site of NP. However, the exchange route for substrate and product between the active site and the solvent is not obvious from the structures. Flexibility of the cap domain might facilitate such exchange. Interestingly, both carboxylesterases show higher structural similarity to meta-cleavage compound (MCP) hydrolases than to other α/β hydrolase fold esterases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Biophysical Chemistry, Centre of Life Sciences, University of Groningen, Nijenborgh 7, 9747 AG Groningen, The Netherlands.