Distinctive Conformation of Minor Site-Specific Nuclear Localization Signals Bound to Importin-Alpha
Chang, C.-W., Counago, R.M., Williams, S.J., Boden, M., Kobe, B.(2013) Traffic 14: 1144
- PubMed: 23910026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12098
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
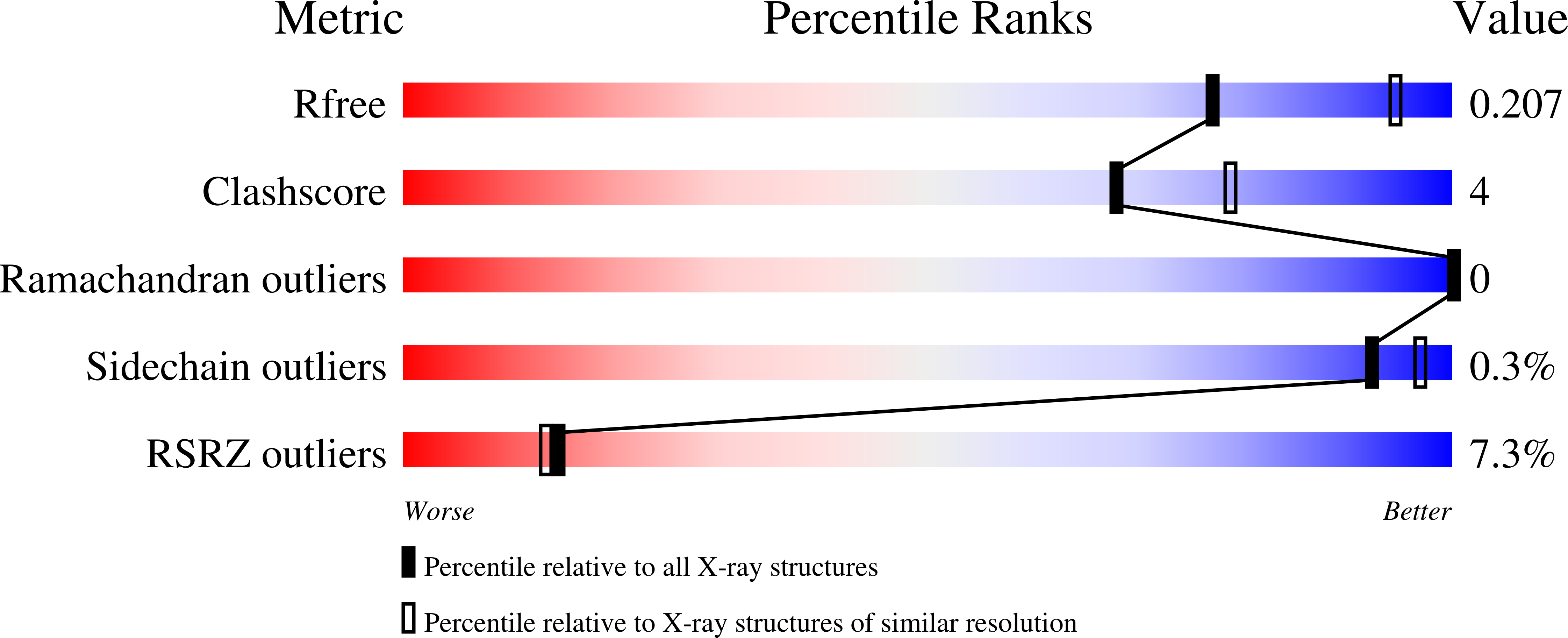
3ZIN, 3ZIO, 3ZIP, 3ZIQ, 3ZIR - PubMed Abstract:
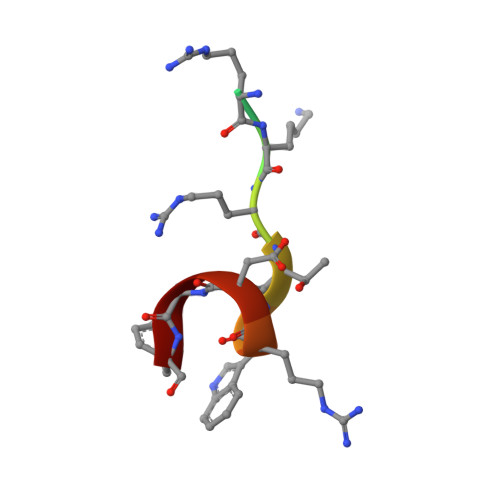
Nuclear localization signals (NLSs) contain one or two clusters of basic residues and are recognized by the import receptor importin-α. There are two NLS-binding sites (major and minor) on importin-α and the major NLS-binding site is considered to be the primary binding site. Here, we used crystallographic and biochemical methods to investigate the binding between importin-α and predicted 'minor site-specific' NLSs: four peptide library-derived peptides, and the NLS from mouse RNA helicase II/Guα. The crystal structures reveal that these atypical NLSs indeed preferentially bind to the minor NLS-binding site. Unlike previously characterized NLSs, the C-terminal residues of these NLSs form an α-helical turn, stabilized by internal H-bond and cation-π interactions between the aromatic residues from the NLSs and the positively charged residues from importin-α. This helical turn sterically hinders binding at the major NLS-binding site, explaining the minor-site preference. Our data suggest the sequence RXXKR[K/X][F/Y/W]XXAF as the optimal minor NLS-binding site-specific motif, which may help identify novel proteins with atypical NLSs.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences and Institute for Molecular Bioscience, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Qld, 4072, Australia; Australian Infectious Diseases Research Centre, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Qld, 4072, Australia.