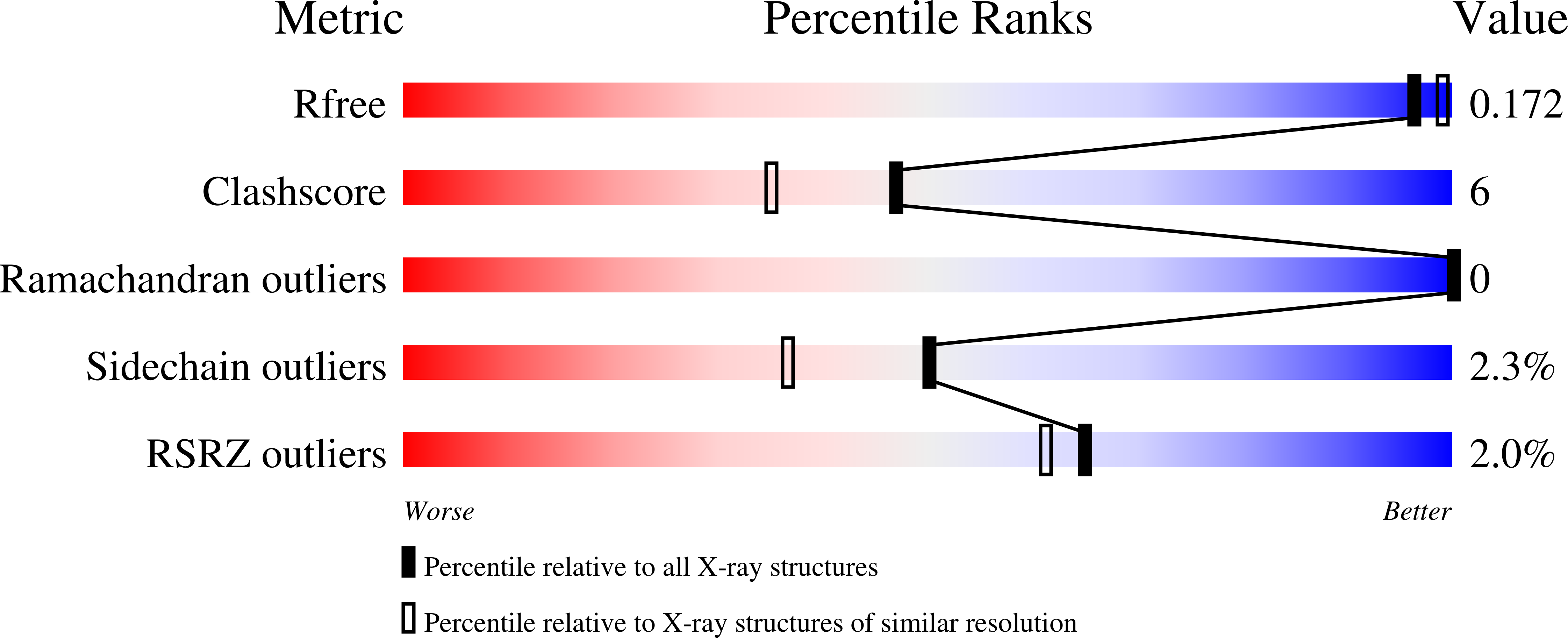
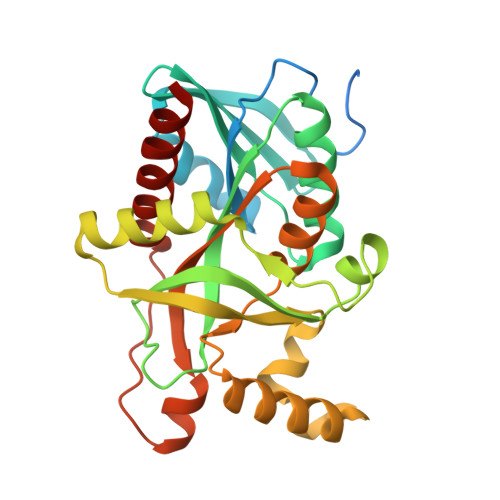
The Crystal Structure of Streptococcus pyogenes Uridine Phosphorylase Reveals a Distinct Subfamily of Nucleoside Phosphorylases.
Tran, T.H., Christoffersen, S., Allan, P.W., Parker, W.B., Serra, I., Terreni, M., Ealick, S.E.(2011) Biochemistry 50: 6549-6558
- PubMed: 21707079
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi200707z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QPB - PubMed Abstract:
Uridine phosphorylase (UP), a key enzyme in the pyrimidine salvage pathway, catalyzes the reversible phosphorolysis of uridine or 2'-deoxyuridine to uracil and ribose 1-phosphate or 2'-deoxyribose 1-phosphate. This enzyme belongs to the nucleoside phosphorylase I superfamily whose members show diverse specificity for nucleoside substrates. Phylogenetic analysis shows Streptococcus pyogenes uridine phosphorylase (SpUP) is found in a distinct branch of the pyrimidine subfamily of nucleoside phosphorylases. To further characterize SpUP, we determined the crystal structure in complex with the products, ribose 1-phosphate and uracil, at 1.8 Å resolution. Like Escherichia coli UP (EcUP), the biological unit of SpUP is a hexamer with an α/β monomeric fold. A novel feature of the active site is the presence of His169, which structurally aligns with Arg168 of the EcUP structure. A second active site residue, Lys162, is not present in previously determined UP structures and interacts with O2 of uracil. Biochemical studies of wild-type SpUP showed that its substrate specificity is similar to that of EcUP, while EcUP is ∼7-fold more efficient than SpUP. Biochemical studies of SpUP mutants showed that mutations of His169 reduced activity, while mutation of Lys162 abolished all activity, suggesting that the negative charge in the transition state resides mostly on uracil O2. This is in contrast to EcUP for which transition state stabilization occurs mostly at O4.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853-1301, United States.