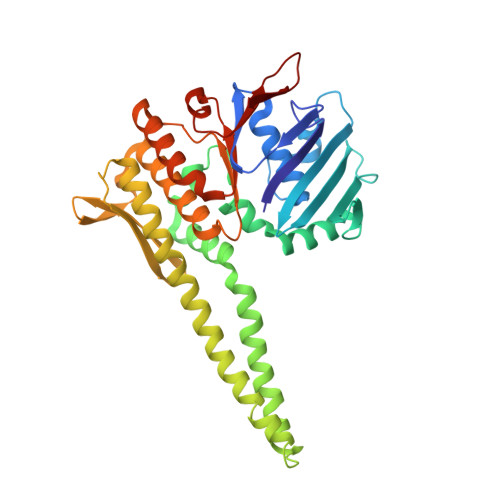
ABC ATPase signature helices in Rad50 link nucleotide state to Mre11 interface for DNA repair.
Williams, G.J., Williams, R.S., Williams, J.S., Moncalian, G., Arvai, A.S., Limbo, O., Guenther, G., Sildas, S., Hammel, M., Russell, P., Tainer, J.A.(2011) Nat Struct Mol Biol 18: 423-431
- PubMed: 21441914
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2038
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QKR, 3QKS, 3QKT, 3QKU - PubMed Abstract:
The Rad50 ABC-ATPase complex with Mre11 nuclease is essential for dsDNA break repair, telomere maintenance and ataxia telangiectasia-mutated kinase checkpoint signaling. How Rad50 affects Mre11 functions and how ABC-ATPases communicate nucleotide binding and ligand states across long distances and among protein partners are questions that have remained obscure. Here, structures of Mre11-Rad50 complexes define the Mre11 2-helix Rad50 binding domain (RBD) that forms a four-helix interface with Rad50 coiled coils adjoining the ATPase core. Newly identified effector and basic-switch helix motifs extend the ABC-ATPase signature motif to link ATP-driven Rad50 movements to coiled coils binding Mre11, implying an ~30-Å pull on the linker to the nuclease domain. Both RBD and basic-switch mutations cause clastogen sensitivity. Our new results characterize flexible ATP-dependent Mre11 regulation, defects in cancer-linked RBD mutations, conserved superfamily basic switches and motifs effecting ATP-driven conformational change, and they provide a unified comprehension of ABC-ATPase activities.
Organizational Affiliation:
Life Sciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California, USA.