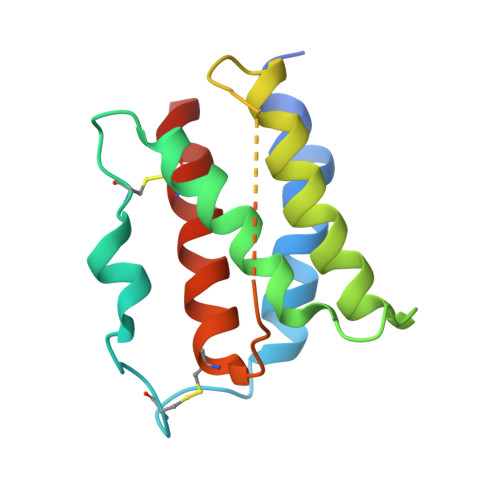
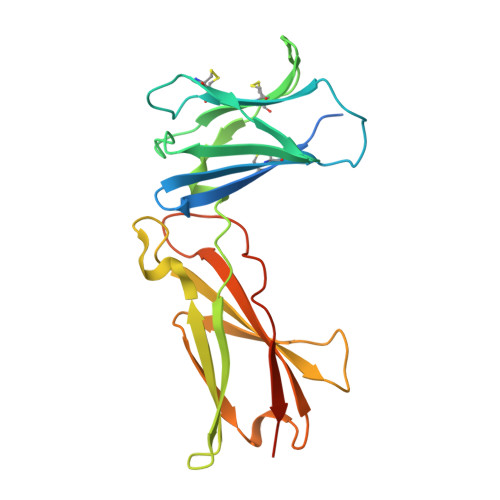
Structural and Biophysical Studies of the Human IL-7/IL-7Ralpha Complex.
McElroy, C.A., Dohm, J.A., Walsh, S.T.(2009) Structure 17: 54-65
- PubMed: 19141282
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2008.10.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DI2, 3DI3 - PubMed Abstract:
IL-7 and IL-7Ralpha bind the gamma(c) receptor, forming a complex crucial to several signaling cascades leading to the development and homeostasis of T and B cells. We report that the IL-7Ralpha ectodomain uses glycosylation to modulate its binding constants to IL-7, unlike the other receptors in the gamma(c) family. IL-7 binds glycosylated IL-7Ralpha 300-fold more tightly than unglycosylated IL-7Ralpha, and the enhanced affinity is attributed primarily to an accelerated on rate. Structural comparison of IL-7 in complex to both forms of IL-7Ralpha reveals that glycosylation does not participate directly in the binding interface. The SCID mutations of IL-7Ralpha locate outside the binding interface with IL-7, suggesting that the expressed mutations cause protein folding defects in IL-7Ralpha. The IL-7/IL-7Ralpha structures provide a window into the molecular recognition events of the IL-7 signaling cascade and provide sites to target for designing new therapeutics to treat IL-7-related diseases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Comprehensive Cancer Center, Ohio State University, 467 Hamilton Hall, 1645 Neil Avenue, Columbus, OH 43210, USA.