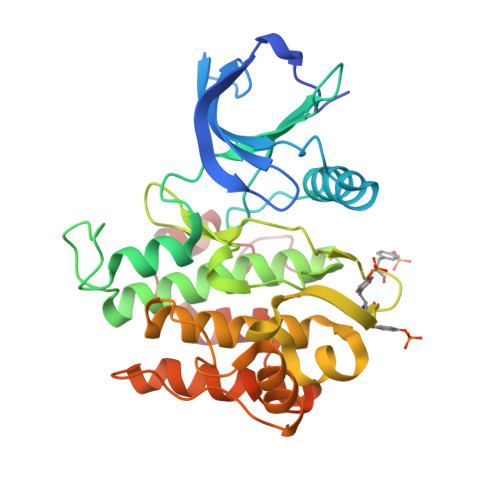
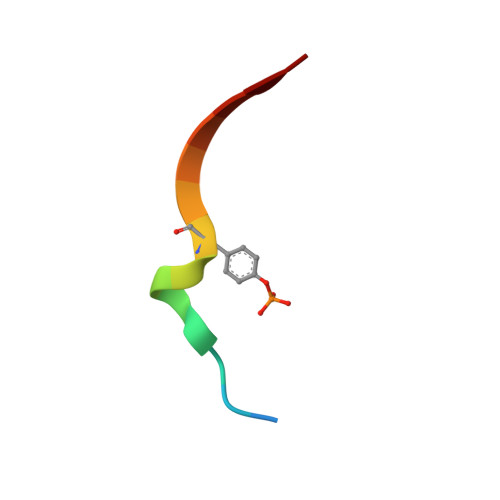
Structural and biochemical characterization of the KRLB region in insulin receptor substrate-2.
Wu, J., Tseng, Y.D., Xu, C.F., Neubert, T.A., White, M.F., Hubbard, S.R.(2008) Nat Struct Mol Biol 15: 251-258
- PubMed: 18278056
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1388
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BU3, 3BU5, 3BU6 - PubMed Abstract:
Insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 (IRS1 and -2) are crucial adaptor proteins in mediating the metabolic and mitogenic effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1. These proteins consist of a pleckstrin homology domain, a phosphotyrosine binding domain and a C-terminal region containing numerous sites of tyrosine, serine and threonine phosphorylation. Previous yeast two-hybrid studies identified a region unique to IRS2, termed the kinase regulatory-loop binding (KRLB) region, which interacts with the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor. Here we present the crystal structure of the insulin receptor kinase in complex with a 15-residue peptide from the KRLB region. In the structure, this segment of IRS2 is bound in the kinase active site with Tyr628 positioned for phosphorylation. Although Tyr628 was phosphorylated by the insulin receptor, its catalytic turnover was poor, resulting in kinase inhibition. Our studies indicate that the KRLB region functions to limit tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS2.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Program, Kimmel Center for Biology and Medicine of the Skirball Institute, and Department of Pharmacology, New York University School of Medicine, 540 First Avenue, New York, New York 10016, USA.