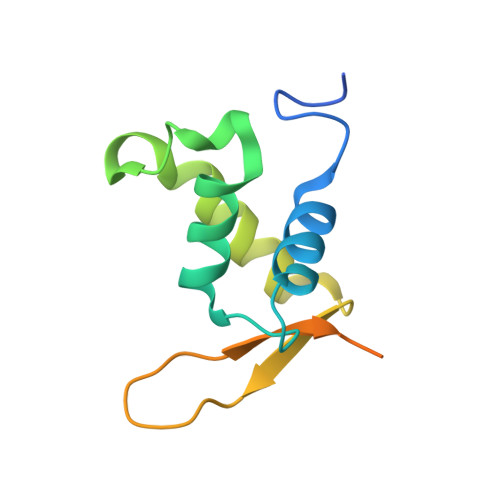
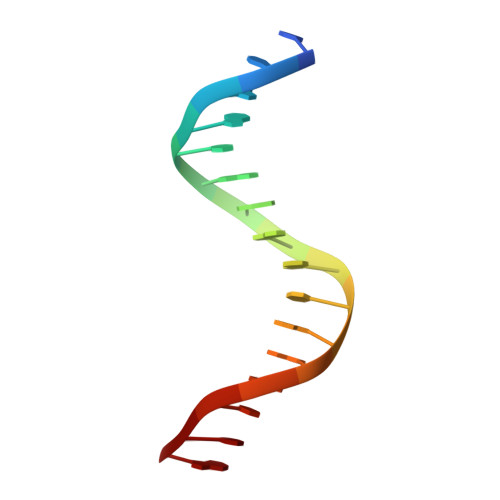
Structural Basis for DNA Recognition by FoxO1 and Its Regulation by Posttranslational Modification.
Brent, M.M., Anand, R., Marmorstein, R.(2008) Structure 16: 1407-1416
- PubMed: 18786403
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2008.06.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3CO6, 3CO7, 3COA - PubMed Abstract:
FoxO transcription factors regulate the transcription of genes that control metabolism, cellular proliferation, stress tolerance, and possibly life span. A number of posttranslational modifications within the forkhead DNA-binding domain regulate FoxO-mediated transcription. We describe the crystal structures of FoxO1 bound to three different DNA elements and measure the change in FoxO1-DNA affinity with acetylation and phosphorylation. The structures reveal additional contacts and increased DNA distortion for the highest affinity DNA site. The flexible wing 2 region of the forkhead domain was not observed in the structures but is necessary for DNA binding, and we show that p300 acetylation in wing 2 reduces DNA affinity. We also show that MST1 phosphorylation of FoxO1 prevents high-affinity DNA binding. The observation that FoxO-DNA affinity varies between response elements and with posttranslational modifications suggests that modulation of FoxO-DNA affinity is an important component of FoxO regulation in health and misregulation in disease.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Wistar Institute, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA; The Department of Chemistry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.