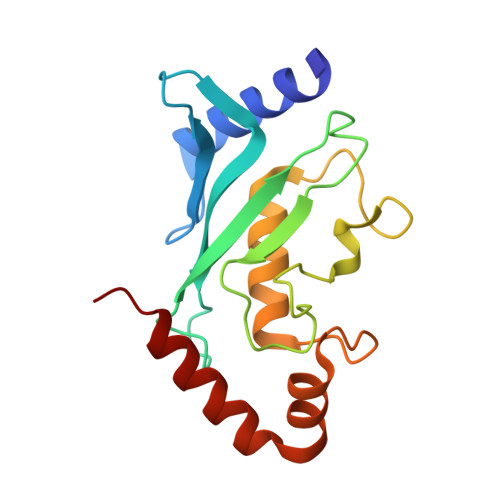
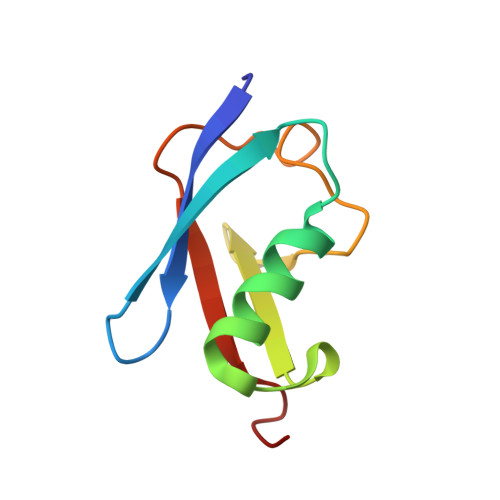
Ubc9 sumoylation regulates SUMO target discrimination.
Knipscheer, P., Flotho, A., Klug, H., Olsen, J.V., van Dijk, W.J., Fish, A., Johnson, E.S., Mann, M., Sixma, T.K., Pichler, A.(2008) Mol Cell 31: 371-382
- PubMed: 18691969
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.022
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VRR - PubMed Abstract:
Posttranslational modification with small ubiquitin-related modifier, SUMO, is a widespread mechanism for rapid and reversible changes in protein function. Considering the large number of known targets, the number of enzymes involved in modification seems surprisingly low: a single E1, a single E2, and a few distinct E3 ligases. Here we show that autosumoylation of the mammalian E2-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 at Lys14 regulates target discrimination. While not altering its activity toward HDAC4, E2-25K, PML, or TDG, sumoylation of Ubc9 impairs its activity on RanGAP1 and strongly activates sumoylation of the transcriptional regulator Sp100. Enhancement depends on a SUMO-interacting motif (SIM) in Sp100 that creates an additional interface with the SUMO conjugated to the E2, a mechanism distinct from Ubc9 approximately SUMO thioester recruitment. The crystal structure of sumoylated Ubc9 demonstrates how the newly created binding interface can provide a gain in affinity otherwise provided by E3 ligases.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Netherlands Cancer Institute and Center for Biomedical Genetics, Plesmanlaan 121, 1066 CX Amsterdam, The Netherlands.