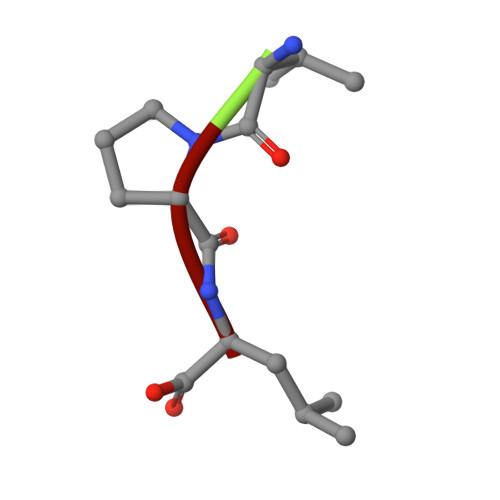
Complexes of Mutants of Escherichia Coli Aminopeptidase P and the Tripeptide Substrate Valproleu.
Graham, S.C., Guss, J.M.(2008) Arch Biochem Biophys 469: 200
- PubMed: 17983589
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2007.10.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2V3X, 2V3Y, 2V3Z - PubMed Abstract:
Aminopeptidase P (APPro) is a manganese-containing enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of the N-terminal residue of a polypeptide if the second residue is proline. Structures of APPro mutants with reduced or negligible activity have been determined in complex with the tripeptide substrate ValProLeu. In the complex of Glu383Ala APPro with ValProLeu one of the two metal sites is only partly occupied, indicating an essential role for Glu383 in metal binding in the presence of substrate. His361Ala APPro clearly possesses residual activity as the ValProLeu substrate has been cleaved in the crystals; difference electron density consistent with bound ProLeu dipeptide and a disordered Val amino acid is present at the active site. Contrary to previous suggestions, the His243Ala mutant is capable of binding substrate. The structure of the His243Ala APPro complex with ValProLeu shows that the peptide interacts with one of the active-site metal atoms via its terminal amino group. The implications of these complexes for the roles of the respective residues in APPro catalysis are discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Biology, The Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX3 7BN, UK.