Phosphorylation-independent interaction between 14-3-3 and exoenzyme S: from structure to pathogenesis
Ottmann, C., Yasmin, L., Weyand, M., Veesenmeyer, J.L., Diaz, M.H., Palmer, R.H., Francis, M.S., Hauser, A.R., Wittinghofer, A., Hallberg, B.(2007) EMBO J 26: 902-913
- PubMed: 17235285
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601530
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2O02 - PubMed Abstract:
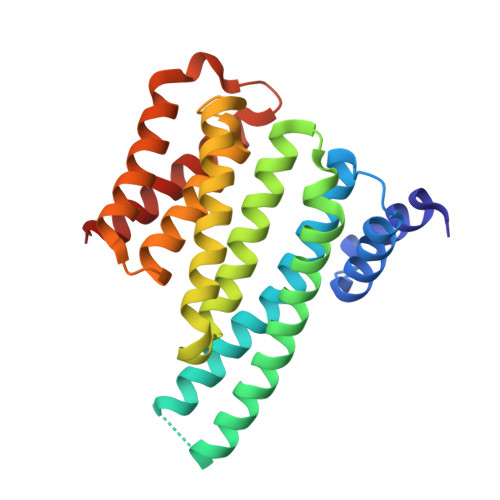
14-3-3 proteins are phosphoserine/phosphothreonine-recognizing adapter proteins that regulate the activity of a vast array of targets. There are also examples of 14-3-3 proteins binding their targets via unphosphorylated motifs. Here we present a structural and biological investigation of the phosphorylation-independent interaction between 14-3-3 and exoenzyme S (ExoS), an ADP-ribosyltransferase toxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ExoS binds to 14-3-3 in a novel binding mode mostly relying on hydrophobic contacts. The 1.5 A crystal structure is supported by cytotoxicity analysis, which reveals that substitution of the corresponding hydrophobic residues significantly weakens the ability of ExoS to modify the endogenous targets RAS/RAP1 and to induce cell death. Furthermore, mutation of key residues within the ExoS binding site for 14-3-3 impairs virulence in a mouse pneumonia model. In conclusion, we show that ExoS binds 14-3-3 in a novel reversed orientation that is primarily dependent on hydrophobic residues. This interaction is phosphorylation independent and is required for the function of ExoS.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Max-Planck-Institute for Molecular Physiology, Dortmund, Germany.