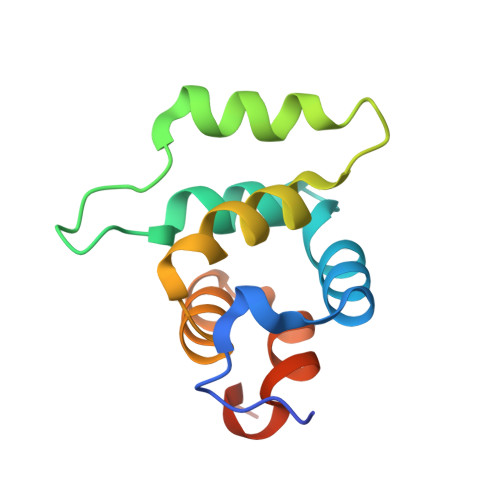
Cutting Edge: Molecular Structure of the IL-1R-Associated Kinase-4 Death Domain and Its Implications for TLR Signaling.
Lasker, M.V., Gajjar, M.M., Nair, S.K.(2005) J Immunol 175: 4175-4179
- PubMed: 16177054
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.175.7.4175
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2A9I - PubMed Abstract:
IL-1R-associated kinase (IRAK) 4 is an essential component of innate immunity. IRAK-4 deficiency in mice and humans results in severe impairment of IL-1 and TLR signaling. We have solved the crystal structure for the death domain of Mus musculus IRAK-4 to 1.7 A resolution. This is the first glimpse of the structural details of a mammalian IRAK family member. The crystal structure reveals a six-helical bundle with a prominent loop, which among IRAKs and Pelle, a Drosophila homologue, is unique to IRAK-4. This highly structured loop contained between helices two and three, comprises an 11-aa stretch. Although innate immune domain recognition is thought to be very similar between Drosophila and mammals, this structural component points to a drastic difference. This structure can be used as a framework for future mutation and deletion studies and potential drug design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Illinois, Urbana 61801, USA.