Structural basis for elastolytic substrate specificity in rodent alpha-chymases.
Kervinen, J., Abad, M., Crysler, C., Kolpak, M., Mahan, A.D., Masucci, J.A., Bayoumy, S., Cummings, M.D., Yao, X., Olson, M., de Garavilla, L., Kuo, L., Deckman, I., Spurlino, J.(2008) J Biol Chem 283: 427-436
- PubMed: 17981788
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M707157200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2RDL - PubMed Abstract:
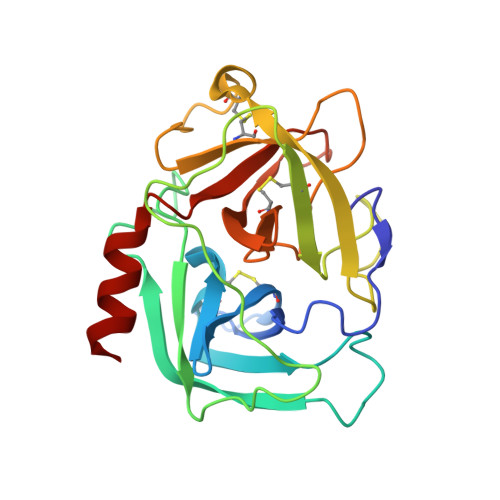
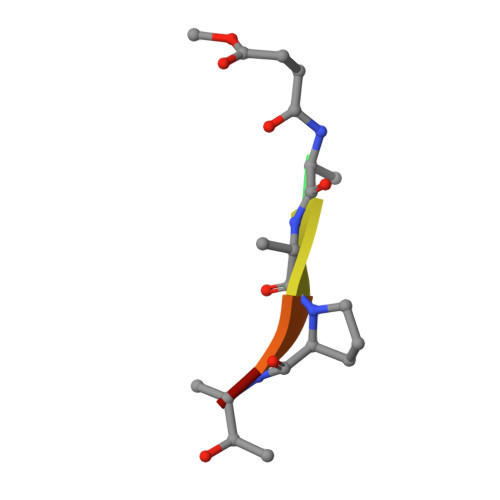
Divergence of substrate specificity within the context of a common structural framework represents an important mechanism by which new enzyme activity naturally evolves. We present enzymological and x-ray structural data for hamster chymase-2 (HAM2) that provides a detailed explanation for the unusual hydrolytic specificity of this rodent alpha-chymase. In enzymatic characterization, hamster chymase-1 (HAM1) showed typical chymase proteolytic activity. In contrast, HAM2 exhibited atypical substrate specificity, cleaving on the carboxyl side of the P1 substrate residues Ala and Val, characteristic of elastolytic rather than chymotryptic specificity. The 2.5-A resolution crystal structure of HAM2 complexed to the peptidyl inhibitor MeOSuc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Ala-chloromethylketone revealed a narrow and shallow S1 substrate binding pocket that accommodated only a small hydrophobic residue (e.g. Ala or Val). The different substrate specificities of HAM2 and HAM1 are explained by changes in four S1 substrate site residues (positions 189, 190, 216, and 226). Of these, Asn(189), Val(190), and Val(216) form an easily identifiable triplet in all known rodent alpha-chymases that can be used to predict elastolytic specificity for novel chymase-like sequences. Phylogenetic comparison defines guinea pig and rabbit chymases as the closest orthologs to rodent alpha-chymases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development, Structural Biology, Exton, Pennsylvania 19341. Electronic address: jkervine@prdus.jnj.com.