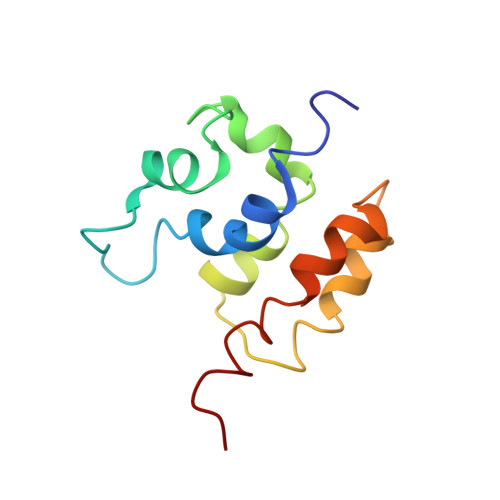
Solution Structure of the COMMD1 N-terminal Domain.
Sommerhalter, M., Zhang, Y., Rosenzweig, A.C.(2007) J Mol Biol 365: 715-721
- PubMed: 17097678
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.10.030
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2H2M - PubMed Abstract:
COMMD1 is the prototype of a new protein family that plays a role in several important cellular processes, including NF-kappaB signaling, sodium transport, and copper metabolism. The COMMD proteins interact with one another via a conserved C-terminal domain, whereas distinct functions are predicted to result from a variable N-terminal domain. The COMMD proteins have not been characterized biochemically or structurally. Here, we present the solution structure of the N-terminal domain of COMMD1 (N-COMMD1, residues 1-108). This domain adopts an alpha-helical structure that bears little resemblance to any other helical protein. The compact nature of N-COMMD1 suggests that full-length COMMD proteins are modular, consistent with specific functional properties for each domain. Interactions between N-COMMD1 and partner proteins may occur via complementary electrostatic surfaces. These data provide a new foundation for biochemical characterization of COMMD proteins and for probing COMMD1 protein-protein interactions at the molecular level.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, and Cell Biology, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208, USA.