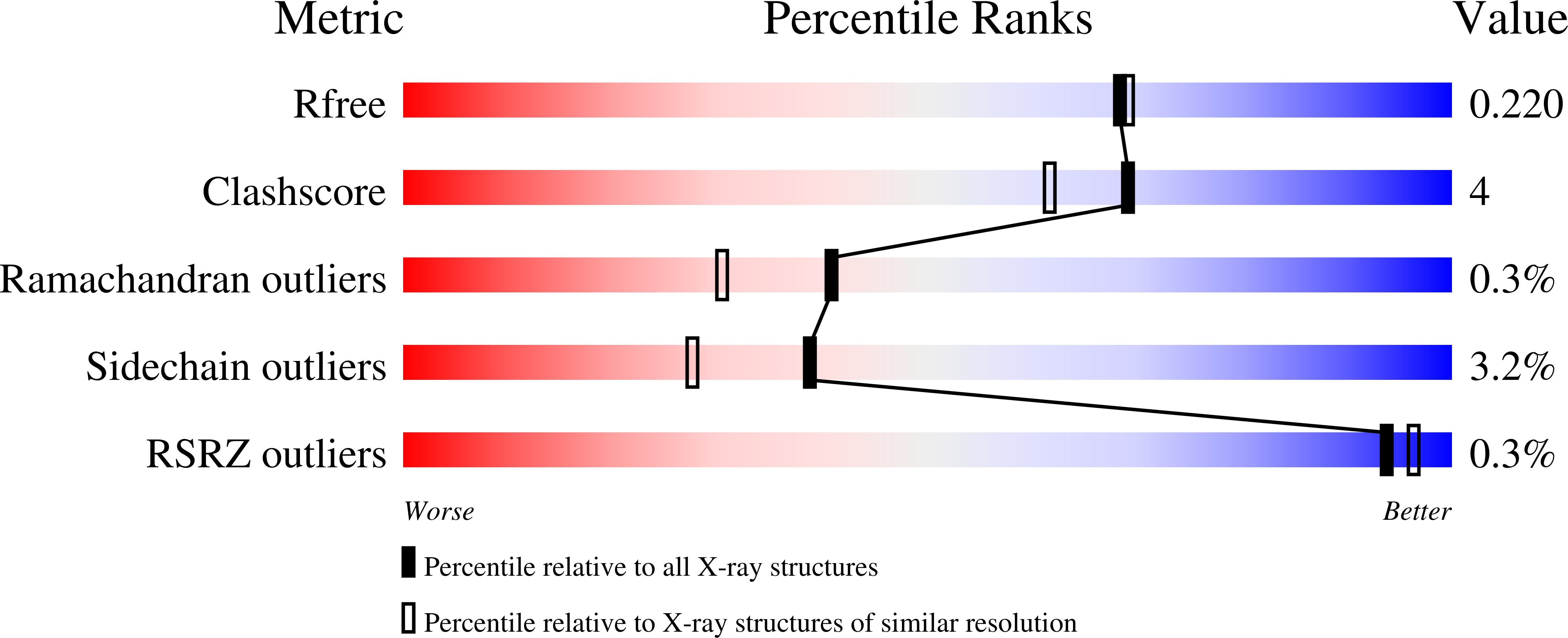
pH-tuneable binding of 2'-phospho-ADP-ribose to ketopantoate reductase: a structural and calorimetric study.
Ciulli, A., Lobley, C.M., Tuck, K.L., Smith, A.G., Blundell, T.L., Abell, C.(2007) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 63: 171-178
- PubMed: 17242510
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444906044465
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YON - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of Escherichia coli ketopantoate reductase in complex with 2'-monophosphoadenosine 5'-diphosphoribose, a fragment of NADP+ that lacks the nicotinamide ring, is reported. The ligand is bound at the enzyme active site in the opposite orientation to that observed for NADP+, with the adenine ring occupying the lipophilic nicotinamide pocket. Isothermal titration calorimetry with R31A and N98A mutants of the enzyme is used to show that the unusual ;reversed binding mode' observed in the crystal is triggered by changes in the protonation of binding groups at low pH. This research has important implications for fragment-based approaches to drug design, namely that the crystallization conditions and the chemical modification of ligands can have unexpected effects on the binding modes.
Organizational Affiliation:
University Chemical Laboratory, Lensfield Road, Cambridge CB2 1EW, England.