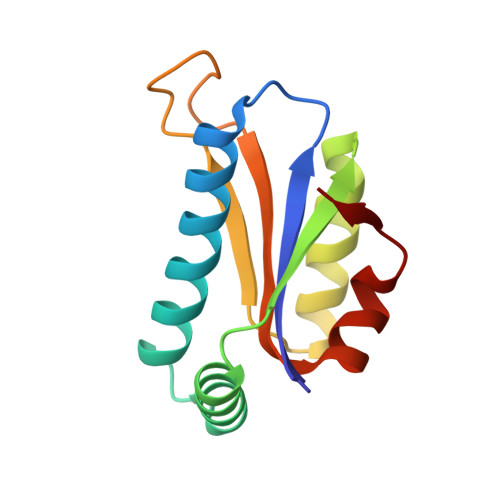
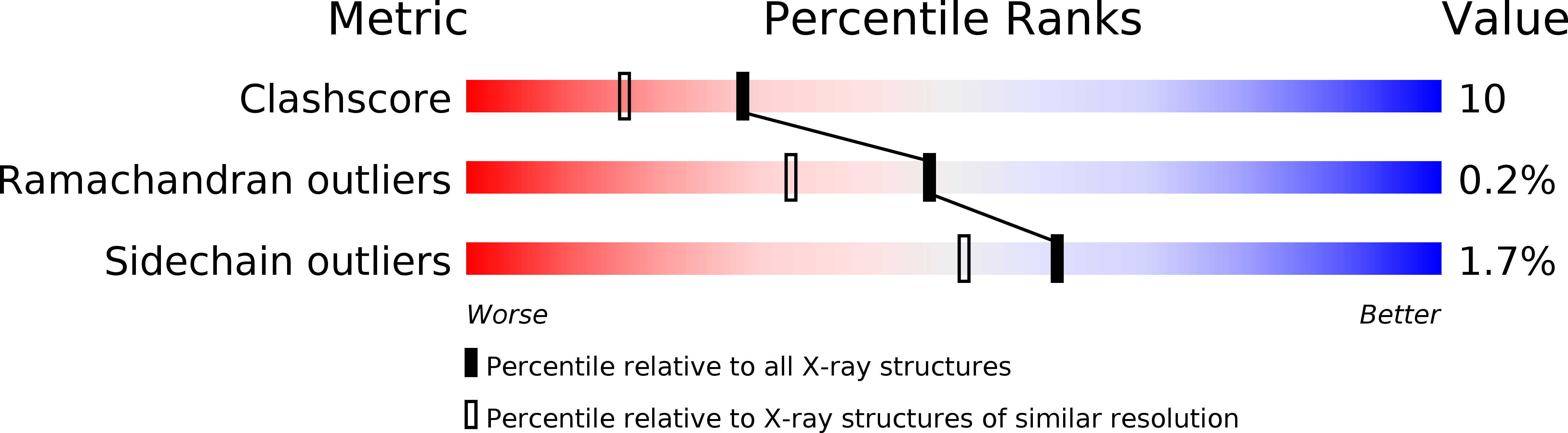Crystal structure at 1.8 A resolution and identification of active site residues of Sulfolobus solfataricus peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase.
Fromant, M., Schmitt, E., Mechulam, Y., Lazennec, C., Plateau, P., Blanquet, S.(2005) Biochemistry 44: 4294-4301
- PubMed: 15766258
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi047711k
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XTY - PubMed Abstract:
The 3-D structure of the peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase from the archaea Sulfolobus solfataricus has been solved at 1.8 A resolution. Homologues of this enzyme are found in archaea and eucarya. Bacteria display a different type of peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase that is also encountered in eucarya. In solution, the S. solfataricus hydrolase behaves as a dimer. In agreement, the crystalline structure of this enzyme indicates the formation of a dimer. Each protomer is made of a mixed five-stranded beta-sheet surrounded by two groups of two alpha-helices. The dimer interface is mainly formed by van der Waals interactions between hydrophobic residues belonging to the two N-terminal alpha1 helices contributed by two protomers. Site-directed mutagenesis experiments were designed for probing the basis of specificity of the archaeal hydrolase. Among the strictly conserved residues within the archaeal/eucaryal peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase family, three residues, K18, D86, and T90, appear of utmost importance for activity. They are located in the N-part of alpha1 and in the beta3-beta4 loop. K18 and D86, which form a salt bridge, might play a role in the catalysis thanks to their acid and basic functions, whereas the OH group of T90 could act as a nucleophile. These observations clearly distinguish the active site of the archaeal/eucaryal hydrolases from that of the bacterial/eucaryal ones, where a histidine is believed to serve as the catalytic base.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratoire de Biochimie, Unité Mixte de Recherche 7654 CNRS-Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau Cedex, France.