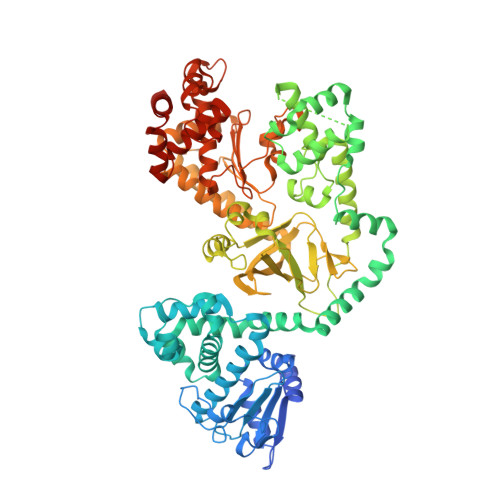
The structural basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity of the anthrax lethal factor.
Turk, B.E., Wong, T.Y., Schwarzenbacher, R., Jarrell, E.T., Leppla, S.H., Collier, R.J., Liddington, R.C., Cantley, L.C.(2004) Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 60-66
- PubMed: 14718924
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb708
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PWQ, 1PWU, 1PWV, 1PWW - PubMed Abstract:
Recent events have created an urgent need for new therapeutic strategies to treat anthrax. We have applied a mixture-based peptide library approach to rapidly determine the optimal peptide substrate for the anthrax lethal factor (LF), a metalloproteinase with an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease. Using this approach we have identified peptide analogs that inhibit the enzyme in vitro and that protect cultured macrophages from LF-mediated cytolysis. The crystal structures of LF bound to an optimized peptide substrate and to peptide-based inhibitors provide a rationale for the observed selectivity and may be exploited in the design of future generations of LF inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Signal Transduction, Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and Harvard Medical School, 330 Brookline Avenue, Boston, Massachusetts 02215, USA.