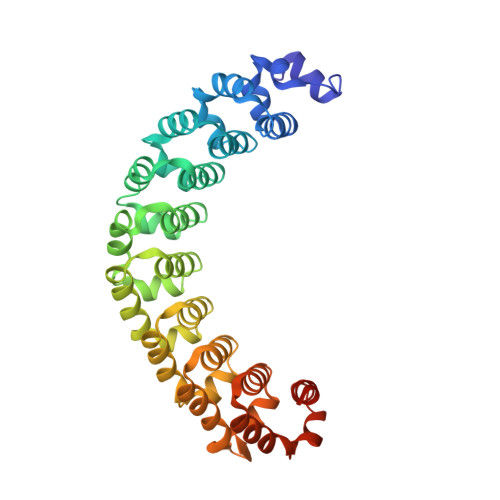MODULAR RECOGNITION OF RNA BY A HUMAN PUMILIO-HOMOLOGY DOMAIN
Wang, X., McLachlan, J., Zamore, P.D., Hall, T.M.T.(2002) Cell 110: 501-512
- PubMed: 12202039
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00873-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1M8W, 1M8X, 1M8Y - PubMed Abstract:
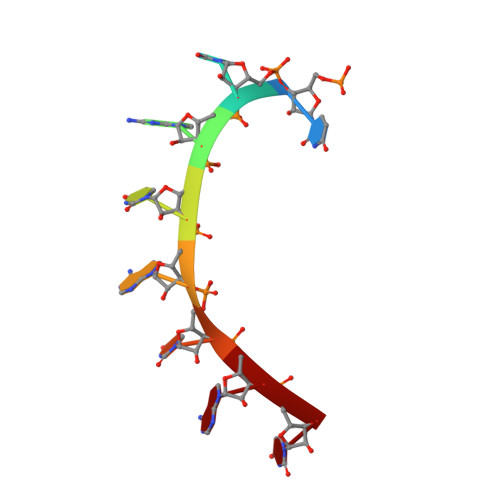
Puf proteins are developmental regulators that control mRNA stability and translation by binding sequences in the 3' untranslated regions of their target mRNAs. We have determined the structure of the RNA binding domain of the human Puf protein, Pumilio1, bound to a high-affinity RNA ligand. The RNA binds the concave surface of the molecule, where each of the protein's eight repeats makes contacts with a different RNA base via three amino acid side chains at conserved positions. We have mutated these three side chains in one repeat, thereby altering the sequence specificity of Pumilio1. Thus, the high affinity and specificity of the PUM-HD for RNA is achieved using multiple copies of a simple repeated motif.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Structural Biology, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709, USA.