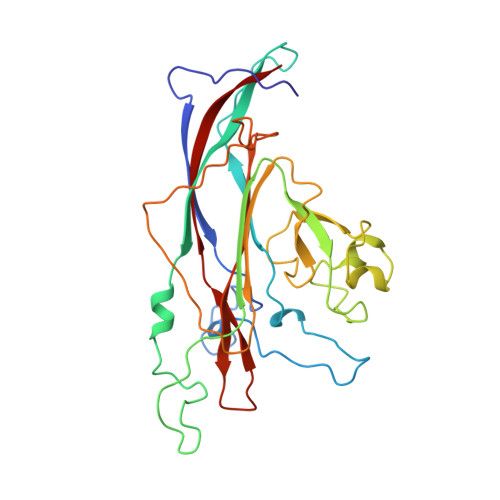
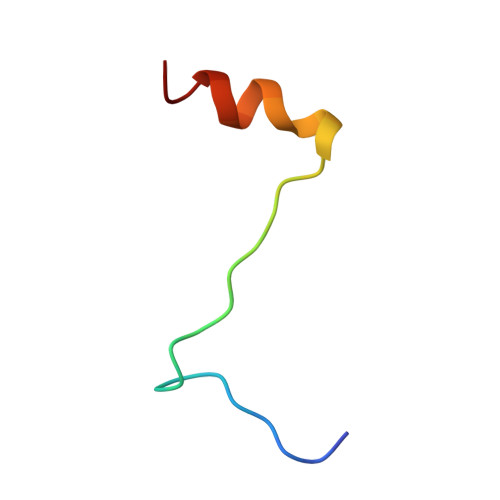
Interaction of polyomavirus internal protein VP2 with the major capsid protein VP1 and implications for participation of VP2 in viral entry.
Chen, X.S., Stehle, T., Harrison, S.C.(1998) EMBO J 17: 3233-3240
- PubMed: 9628860
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/17.12.3233
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1CN3 - PubMed Abstract:
A complex of the polyomavirus internal protein VP2/VP3 with the pentameric major capsid protein VP1 has been prepared by co-expression in Escherichia coli. A C-terminal segment of VP2/VP3 is required for tight association, and a crystal structure of this segment, complexed with a VP1 pentamer, has been determined at 2.2 A resolution. The structure shows specific contacts between a single copy of the internal protein and a pentamer of VP1. These interactions were not detected in the previously described structure of the virion, but the location of VP2 in the recombinant complex is consistent with features in the virion electron-density map. The C-terminus of VP2/VP3 inserts in an unusual, hairpin-like manner into the axial cavity of the VP1 pentamer, where it is anchored strongly by hydrophobic interactions. The remainder of the internal protein appears to have significant flexibility. This structure restricts possible models for exposure of the internal proteins during viral entry.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Harvard University, Boston, MA 02138, USA.