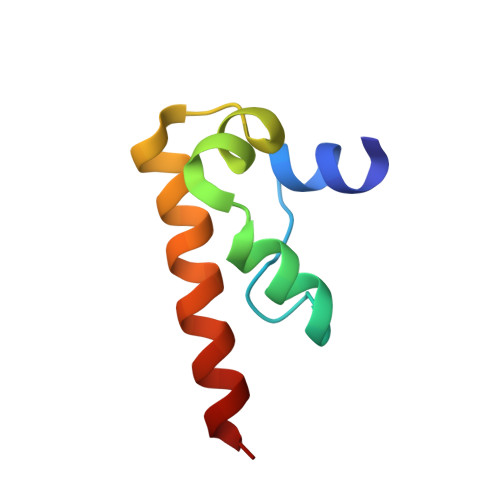
Solution structure of the DFF-C domain of DFF45/ICAD. A structural basis for the regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation.
Fukushima, K., Kikuchi, J., Koshiba, S., Kigawa, T., Kuroda, Y., Yokoyama, S.(2002) J Mol Biol 321: 317-327
- PubMed: 12144788
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00588-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IYR, 1KOY - PubMed Abstract:
DFF45/ICAD has dual functions in the final stage of apoptosis, by acting as both a folding chaperone and a DNase inhibitor of DFF40/CAD. Here, we present the solution structure of the C-terminal domain of DFF45, which is essential for its chaperone-like activity. The structure of this domain (DFF-C) consists of four alpha helices, which are folded in a novel helix-packing arrangement. The 3D structure reveals a large cluster of negatively charged residues on the molecular surface of DFF-C. This observation suggests that charge complementation plays an important role in the interaction of DFF-C with the positively charged catalytic domain of DFF40, and thus for the chaperone activity of DFF45. The structure of DFF-C also provides a rationale for the loss of the chaperone activity in DFF35, a short isoform of DFF45. Indeed, in DFF35, the amino acid sequence is truncated in the middle of the second alpha helix constituting the structure of DFF-C, and thus both the hydrophobic core and the cluster of negative charges are disrupted.
Organizational Affiliation:
Protein Research Group, Genomic Sciences Center, RIKEN Yokohama Institute, 1-7-22, Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi, Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan.