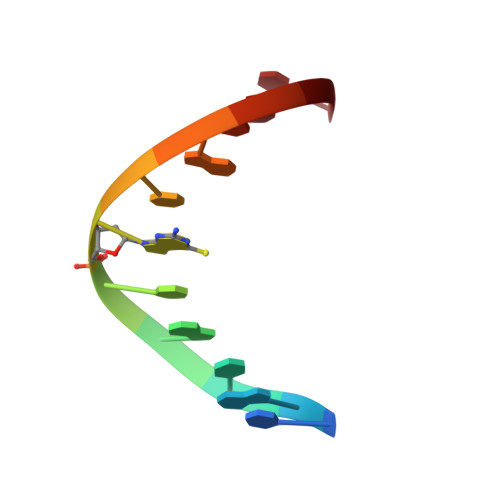
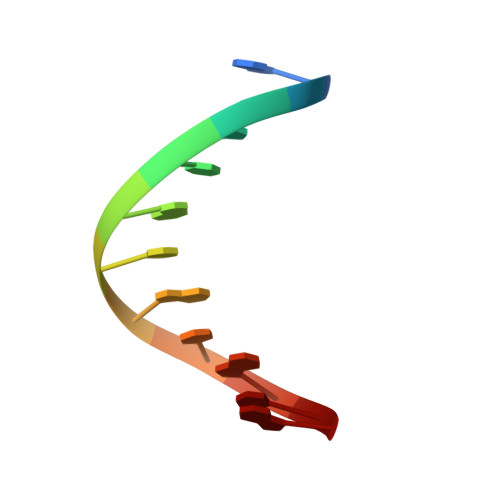
Structural effect of the anticancer agent 6-thioguanine on duplex DNA.
Bohon, J., de los Santos, C.R.(2003) Nucleic Acids Res 31: 1331-1338
- PubMed: 12582253
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg203
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KB1, 1KBM - PubMed Abstract:
The incorporation of 6-thioguanine (S6G) into DNA is an essential step in the cytotoxic activity of thiopurines. However, the structural effects of this substitution on duplex DNA have not been fully characterized. Here, we present the solution structures of DNA duplexes containing S6G opposite thymine (S6G.T) and opposite cytosine (S6G.C), solved by high-resolution NMR spectroscopy and restrained molecular dynamics. The data indicate that both duplexes adopt right-handed helical conformations with all Watson-Crick hydrogen bonding in place. The S6G.T structures exhibit a wobble-type base pairing at the lesion site, with thymine shifted toward the major groove and S6G displaced toward the minor groove. Aside from the lesion site, the helices, including the flanking base pairs, are not highly perturbed by the presence of the lesion. Surprisingly, thermal dependence experiments suggest greater stability in the S6G-T mismatch than the S6G-C base pair.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook, NY 11794-8651, USA.