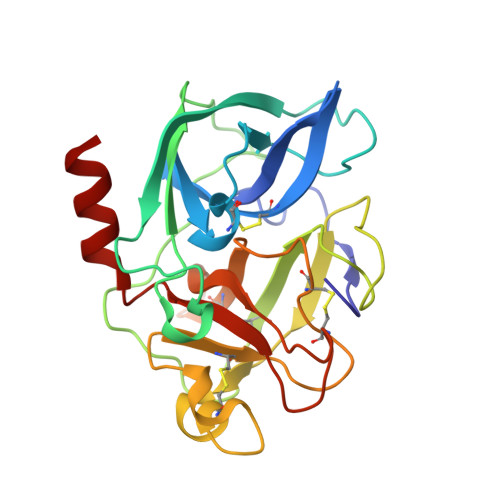
X-Ray Structure of a Serine Protease Acyl-Enzyme Complex at 0.95-A Resolution.
Katona, G., Wilmouth, R.C., Wright, P.A., Berglund, G.I., Hajdu, J., Neutze, R., Schofield, C.J.(2002) J Biol Chem 277: 21962
- PubMed: 11896054
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M200676200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1GVK - PubMed Abstract:
Kinetic analyses led to the discovery that N-acetylated tripeptides with polar residues at P3 are inhibitors of porcine pancreatic elastase (PPE) that form unusually stable acyl-enzyme complexes. Peptides terminating in a C-terminal carboxylate were more potent than those terminating in a C-terminal amide, suggesting recognition by the oxy-anion hole is important in binding. X-ray diffraction data were recorded to 0.95-A resolution for an acyl-enzyme complex formed between PPE and N-acetyl-Asn-Pro-Ile-CO2H at approximately pH 5. The accuracy of the crystallographic coordinates allows structural issues concerning the mechanism of serine proteases to be addressed. Significantly, the ester bond of the acyl-enzyme showed a high level of planarity, suggesting geometric strain of the ester link is not important during catalysis. Several hydrogen atoms could be clearly identified and were included within the model. In keeping with a recent x-ray structure of subtilisin at 0.78 A (1), limited electron density is visible consistent with the putative location of a hydrogen atom approximately equidistant between the histidine and aspartate residues of the catalytic triad. Comparison of this high resolution crystal structure of the acyl-enzyme complex with that of native elastase at 1.1 A (2) showed that binding of the N-terminal part of the substrate can be accommodated with negligible structural rearrangements. In contrast, comparison with structures obtained as part of "time-resolved" studies on the reacting acyl-enzyme complex at >pH 7 (3) indicate small but significant structural differences, consistent with the proposed synchronization of ester hydrolysis and substrate release.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biotechnology, Chalmers University of Technology, Box 462, 40530 Gothenburg, Sweden.