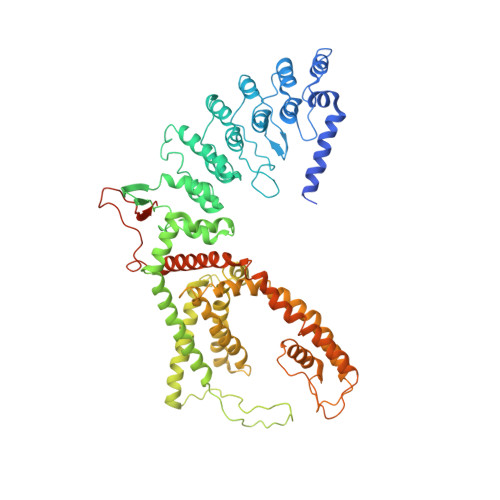
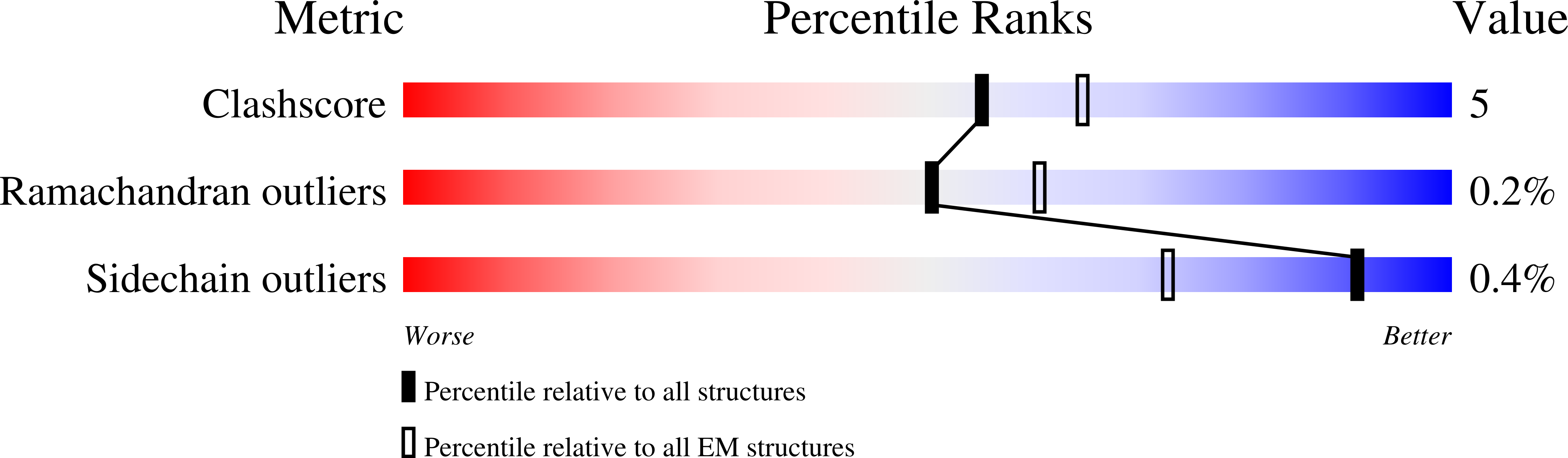Inactivation-mimicking block of the epithelial calcium channel TRPV6.
Bhardwaj, R., Lindinger, S., Neuberger, A., Nadezhdin, K.D., Singh, A.K., Cunha, M.R., Derler, I., Gyimesi, G., Reymond, J.L., Hediger, M.A., Romanin, C., Sobolevsky, A.I.(2020) Sci Adv 6
- PubMed: 33246965
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abe1508
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7D2K, 7K4A, 7K4B, 7K4C, 7K4D, 7K4E, 7K4F - PubMed Abstract:
Epithelial calcium channel TRPV6 plays vital roles in calcium homeostasis, and its dysregulation is implicated in multifactorial diseases, including cancers. Here, we study the molecular mechanism of selective nanomolar-affinity TRPV6 inhibition by (4-phenylcyclohexyl)piperazine derivatives (PCHPDs). We use x-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy to solve the inhibitor-bound structures of TRPV6 and identify two types of inhibitor binding sites in the transmembrane region: (i) modulatory sites between the S1-S4 and pore domains normally occupied by lipids and (ii) the main site in the ion channel pore. Our structural data combined with mutagenesis, functional and computational approaches suggest that PCHPDs plug the open pore of TRPV6 and convert the channel into a nonconducting state, mimicking the action of calmodulin, which causes inactivation of TRPV6 channels under physiological conditions. This mechanism of inhibition explains the high selectivity and potency of PCHPDs and opens up unexplored avenues for the design of future-generation biomimetic drugs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Nephrology and Hypertension and Department of Biomedical Research, University of Bern, Inselspital, Freiburgstrasse 15, CH-3010 Bern, Switzerland.