Discovery and Characterization of 2,5-Substituted Benzoic Acid Dual Inhibitors of the Anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 and Bfl-1 Proteins.
Kump, K.J., Miao, L., Mady, A.S.A., Ansari, N.H., Shrestha, U.K., Yang, Y., Pal, M., Liao, C., Perdih, A., Abulwerdi, F.A., Chinnaswamy, K., Meagher, J.L., Carlson, J.M., Khanna, M., Stuckey, J.A., Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.(2020) J Med Chem 63: 2489-2510
- PubMed: 31971799
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01442
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
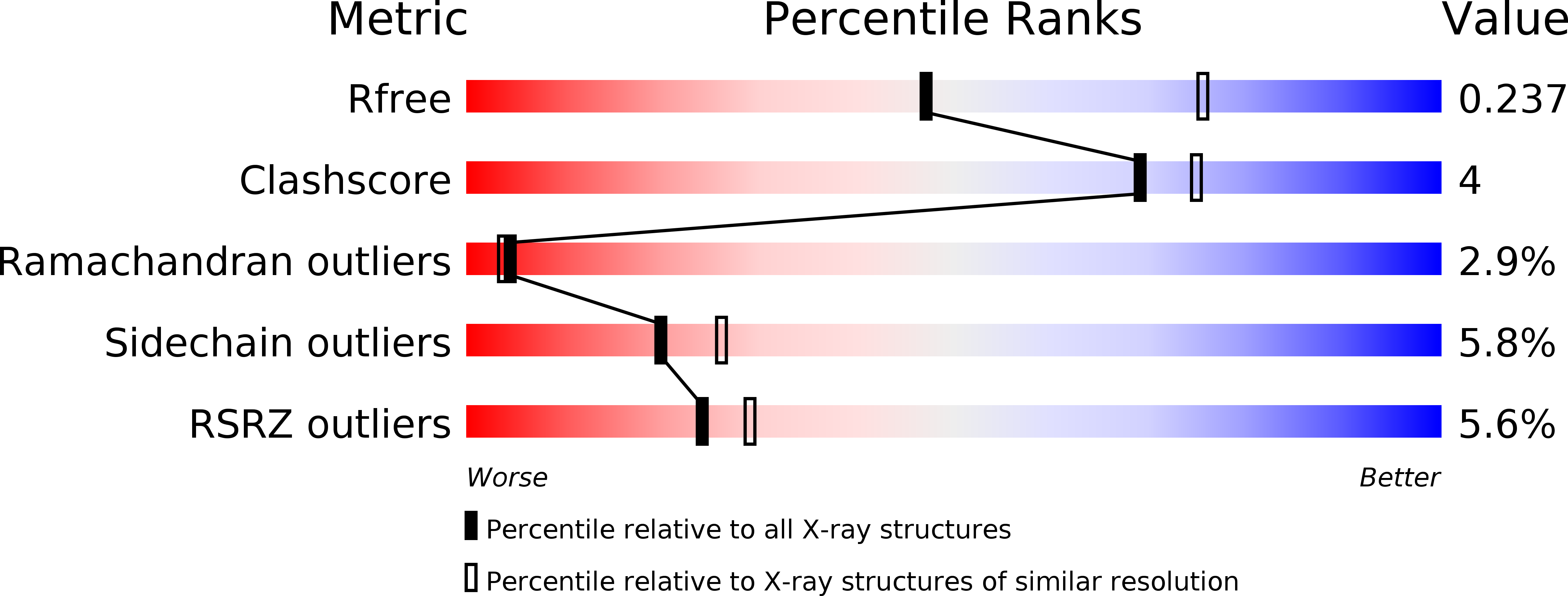
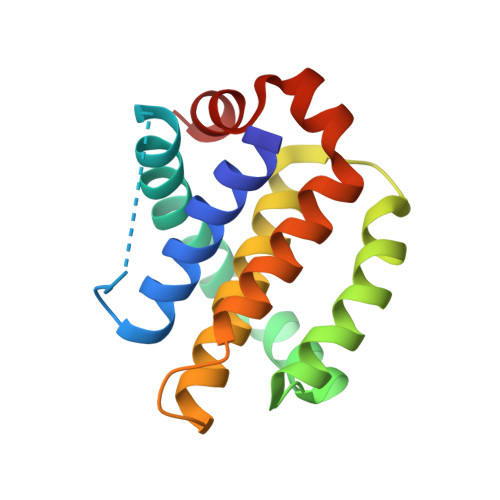
6U63, 6U64, 6U65, 6U67, 6U6F - PubMed Abstract:
Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins are overexpressed in a wide spectrum of cancers and have become well validated therapeutic targets. Cancer cells display survival dependence on individual or subsets of anti-apoptotic proteins that could be effectively targeted by multimodal inhibitors. We designed a 2,5-substituted benzoic acid scaffold that displayed equipotent binding to Mcl-1 and Bfl-1. Structure-based design was guided by several solved cocrystal structures with Mcl-1, leading to the development of compound 24 , which binds both Mcl-1 and Bfl-1 with K i values of 100 nM and shows appreciable selectivity over Bcl-2/Bcl-xL. The selective binding profile of 24 was translated to on-target cellular activity in model lymphoma cell lines. These studies lay a foundation for developing more advanced dual Mcl-1/Bfl-1 inhibitors that have potential to provide greater single agent efficacy and broader coverage to combat resistance in several types of cancer than selective Mcl-1 inhibitors alone.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Institute of Chemistry, Ljubljana 1000, Slovenia.