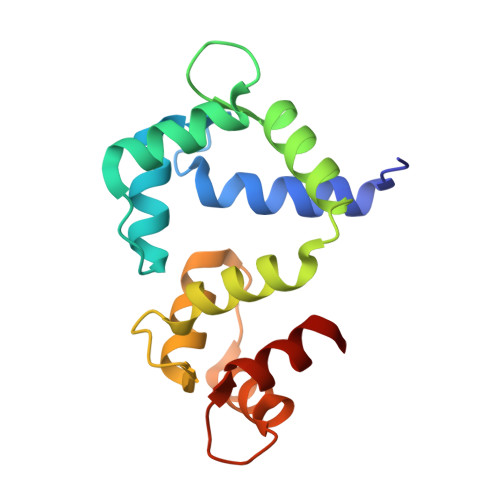
Arrhythmia mutations in calmodulin can disrupt cooperativity of Ca2+binding and cause misfolding.
Wang, K., Brohus, M., Holt, C., Overgaard, M.T., Wimmer, R., Van Petegem, F.(2020) J Physiol 598: 1169-1186
- PubMed: 32012279
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1113/JP279307
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6U39, 6U3A, 6U3B, 6U3D - PubMed Abstract:
Mutations in the calmodulin protein (CaM) are associated with arrhythmia syndromes. This study focuses on understanding the structural characteristics of CaM disease mutants and their interactions with the voltage-gated calcium channel Ca V 1.2. Arrhythmia mutations in CaM can lead to loss of Ca 2+ binding, uncoupling of Ca 2+ binding cooperativity, misfolding of the EF-hands and altered affinity for the calcium channel. These results help us to understand how different CaM mutants have distinct effects on structure and interactions with protein targets to cause disease. Calmodulinopathies are life-threatening arrhythmia syndromes that arise from mutations in calmodulin (CaM), a calcium sensing protein whose sequence is completely conserved across all vertebrates. These mutations have been shown to interfere with the function of cardiac ion channels, including the voltage-gated Ca 2+ channel Ca V 1.2 and the ryanodine receptor (RyR2), in a mutation-specific manner. The ability of different CaM disease mutations to discriminate between these channels has been enigmatic. We present crystal structures of several C-terminal lobe mutants and an N-terminal lobe mutant in complex with the Ca V 1.2 IQ domain, in conjunction with binding assays and complementary structural biology techniques. One mutation (D130G) causes a pathological conformation, with complete separation of EF-hands within the C-lobe and loss of Ca 2+ binding in EF-hand 4. Another variant (Q136P) has severely reduced affinity for the IQ domain, and shows changes in the CD spectra under Ca 2+ -saturating conditions when unbound to the IQ domain. Ca 2+ binding to a pair of EF-hands normally proceeds with very high cooperativity, but we found that N98S CaM can adopt different conformations with either one or two Ca 2+ ions bound to the C-lobe, possibly disrupting the cooperativity. An N-lobe variant (N54I), which causes severe stress-induced arrhythmia, does not show any major changes in complex with the IQ domain, providing a structural basis for why this mutant does not affect function of Ca V 1.2. These findings show that different CaM mutants have distinct effects on both the CaM structure and interactions with protein targets, and act via distinct pathological mechanisms to cause disease.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Life Sciences Institute, University of British Columbia, V6T 1Z3 Vancouver, BC, Canada.