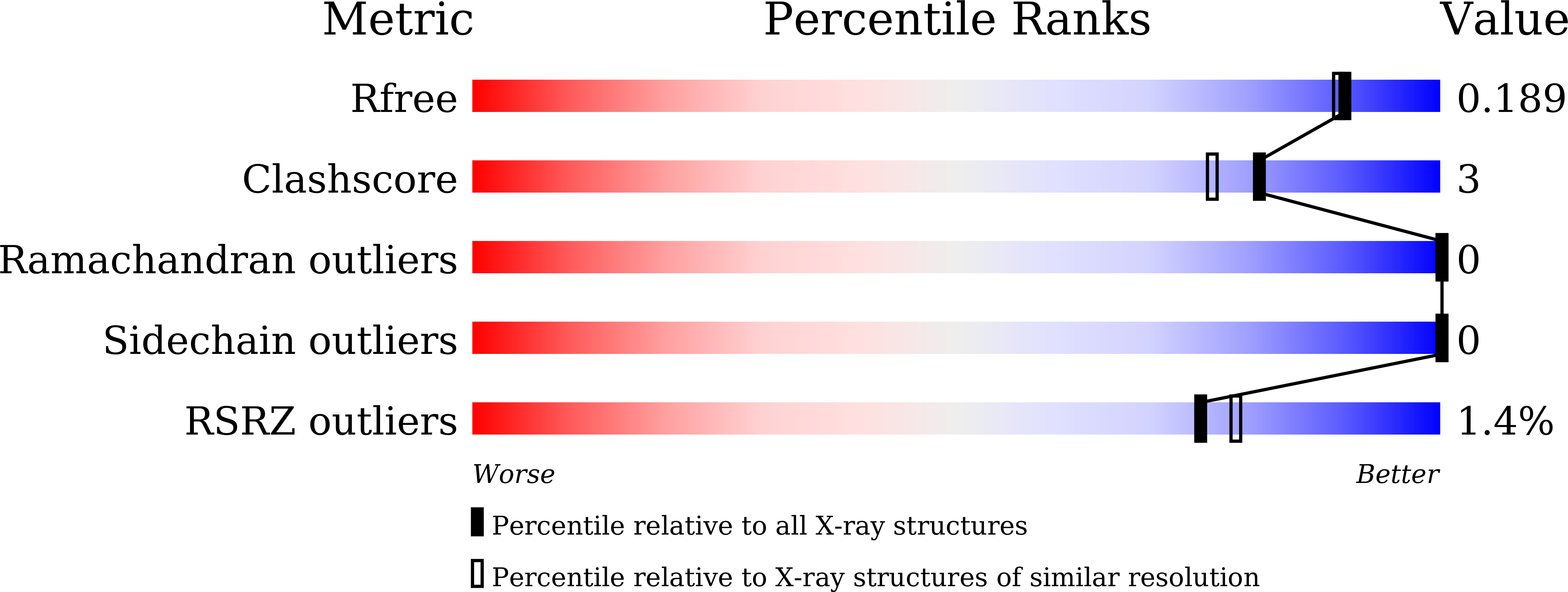
Two distinct modes of DNMT1 recruitment ensure stable maintenance DNA methylation.
Nishiyama, A., Mulholland, C.B., Bultmann, S., Kori, S., Endo, A., Saeki, Y., Qin, W., Trummer, C., Chiba, Y., Yokoyama, H., Kumamoto, S., Kawakami, T., Hojo, H., Nagae, G., Aburatani, H., Tanaka, K., Arita, K., Leonhardt, H., Nakanishi, M.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 1222-1222
- PubMed: 32144273
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15006-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6IIW - PubMed Abstract:
Stable inheritance of DNA methylation is critical for maintaining differentiated phenotypes in multicellular organisms. We have recently identified dual mono-ubiquitylation of histone H3 (H3Ub2) by UHRF1 as an essential mechanism to recruit DNMT1 to chromatin. Here, we show that PCNA-associated factor 15 (PAF15) undergoes UHRF1-dependent dual mono-ubiquitylation (PAF15Ub2) on chromatin in a DNA replication-coupled manner. This event will, in turn, recruit DNMT1. During early S-phase, UHRF1 preferentially ubiquitylates PAF15, whereas H3Ub2 predominates during late S-phase. H3Ub2 is enhanced under PAF15 compromised conditions, suggesting that H3Ub2 serves as a backup for PAF15Ub2. In mouse ES cells, loss of PAF15Ub2 results in DNA hypomethylation at early replicating domains. Together, our results suggest that there are two distinct mechanisms underlying replication timing-dependent recruitment of DNMT1 through PAF15Ub2 and H3Ub2, both of which are prerequisite for high fidelity DNA methylation inheritance.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Cancer Cell Biology, The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, 4-6-1 Shirokanedai, Minato-ku, Tokyo, Japan. anishiya@ims.u-tokyo.ac.jp.