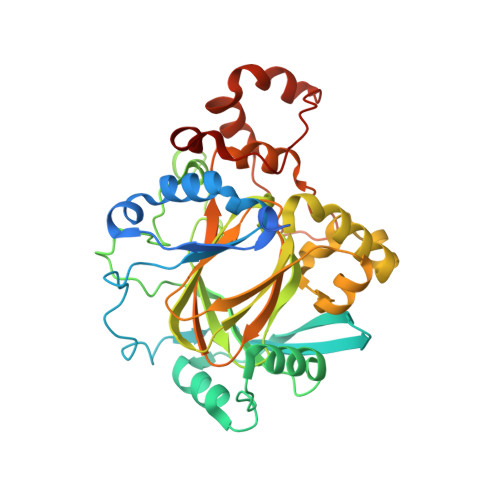
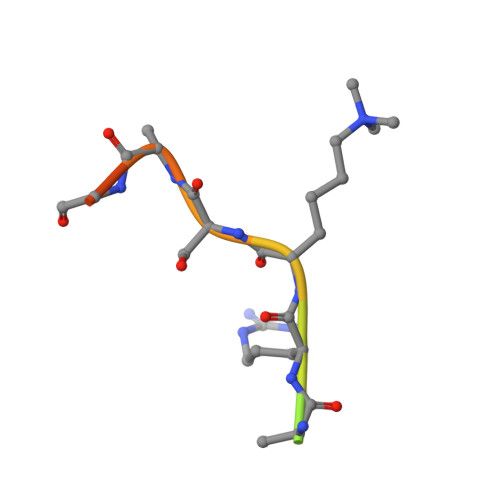
Mechanistic and structural studies of KDM-catalysed demethylation of histone 1 isotype 4 at lysine 26.
Walport, L.J., Hopkinson, R.J., Chowdhury, R., Zhang, Y., Bonnici, J., Schiller, R., Kawamura, A., Schofield, C.J.(2018) FEBS Lett 592: 3264-3273
- PubMed: 30156264
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13231
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6H8P - PubMed Abstract:
N-Methylation of lysyl residues is widely observed on histone proteins. Using isolated enzymes, we report mechanistic and structural studies on histone lysine demethylase (KDM)-catalysed demethylation of N ε -methylated lysine 26 on histone 1 isotype 4 (H1.4). The results reveal that methylated H1.4K26 is a substrate for all members of the KDM4 subfamily and that KDM4A-catalysed demethylation of H1.4K26me3 peptide is similarly efficient to that of H3K9me3. Crystallographic studies of an H1.4K26me3:KDM4A complex reveal a conserved binding geometry to that of H3K9me3. In the light of the high activity of the KDM4s on this mark, our results suggest JmjC KDM-catalysed demethylation of H1.4K26 may be as prevalent as demethylation on the H3 tail and warrants further investigation in cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Chemistry Research Laboratory, University of Oxford, UK.