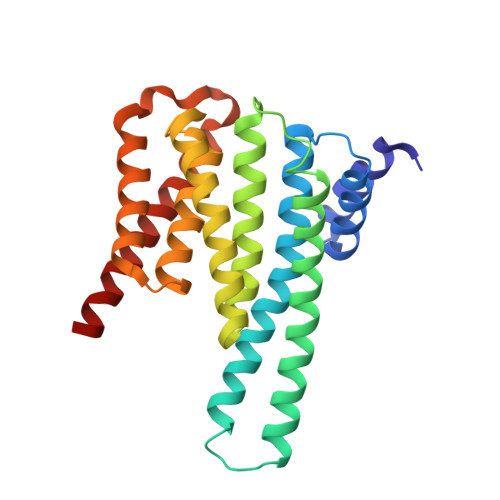
Structural basis of O-GlcNAc recognition by mammalian 14-3-3 proteins.
Toleman, C.A., Schumacher, M.A., Yu, S.H., Zeng, W., Cox, N.J., Smith, T.J., Soderblom, E.J., Wands, A.M., Kohler, J.J., Boyce, M.(2018) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115: 5956-5961
- PubMed: 29784830
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1722437115
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BYJ, 6BYK, 6BYL, 6BZD - PubMed Abstract:
O-GlcNAc is an intracellular posttranslational modification that governs myriad cell biological processes and is dysregulated in human diseases. Despite this broad pathophysiological significance, the biochemical effects of most O-GlcNAcylation events remain uncharacterized. One prevalent hypothesis is that O-GlcNAc moieties may be recognized by "reader" proteins to effect downstream signaling. However, no general O-GlcNAc readers have been identified, leaving a considerable gap in the field. To elucidate O-GlcNAc signaling mechanisms, we devised a biochemical screen for candidate O-GlcNAc reader proteins. We identified several human proteins, including 14-3-3 isoforms, that bind O-GlcNAc directly and selectively. We demonstrate that 14-3-3 proteins bind O-GlcNAc moieties in human cells, and we present the structures of 14-3-3β/α and γ bound to glycopeptides, providing biophysical insights into O-GlcNAc-mediated protein-protein interactions. Because 14-3-3 proteins also bind to phospho-serine and phospho-threonine, they may integrate information from O-GlcNAc and O-phosphate signaling pathways to regulate numerous physiological functions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC 27710.