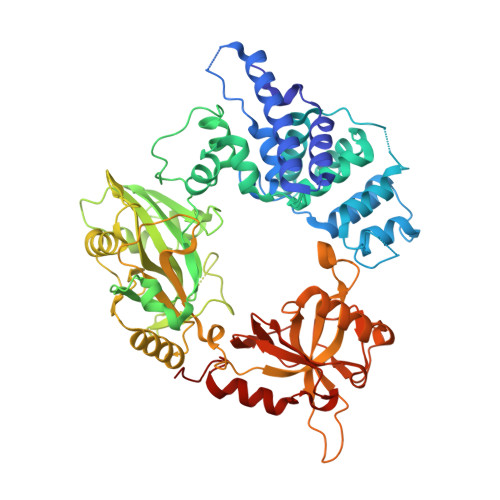
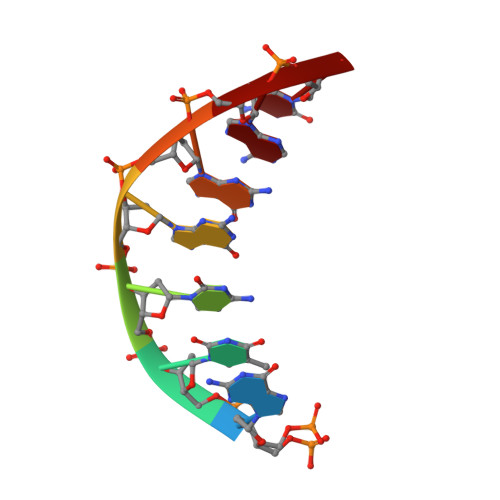
Structures of DNA-bound human ligase IV catalytic core reveal insights into substrate binding and catalysis.
Kaminski, A.M., Tumbale, P.P., Schellenberg, M.J., Williams, R.S., Williams, J.G., Kunkel, T.A., Pedersen, L.C., Bebenek, K.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 2642-2642
- PubMed: 29980672
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05024-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BKF, 6BKG - PubMed Abstract:
DNA ligase IV (LigIV) performs the final DNA nick-sealing step of classical nonhomologous end-joining, which is critical for immunoglobulin gene maturation and efficient repair of genotoxic DNA double-strand breaks. Hypomorphic LigIV mutations cause extreme radiation sensitivity and immunodeficiency in humans. To better understand the unique features of LigIV function, here we report the crystal structure of the catalytic core of human LigIV in complex with a nicked nucleic acid substrate in two distinct states-an open lysyl-AMP intermediate, and a closed DNA-adenylate form. Results from structural and mutagenesis experiments unveil a dynamic LigIV DNA encirclement mechanism characterized by extensive interdomain interactions and active site phosphoanhydride coordination, all of which are required for efficient DNA nick sealing. These studies provide a scaffold for defining impacts of LigIV catalytic core mutations and deficiencies in human LIG4 syndrome.
Organizational Affiliation:
Genome Integrity and Structural Biology Laboratory, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Research Triangle Park, 27709, NC, USA.