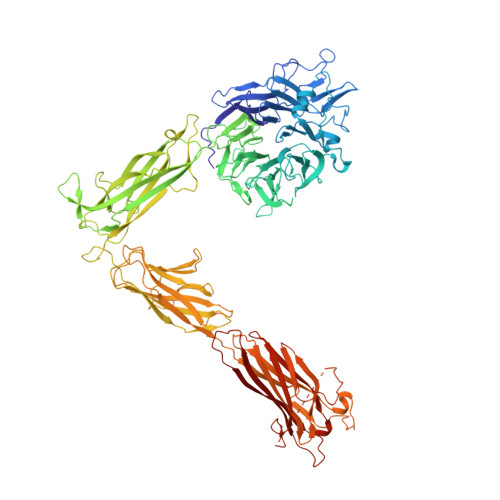
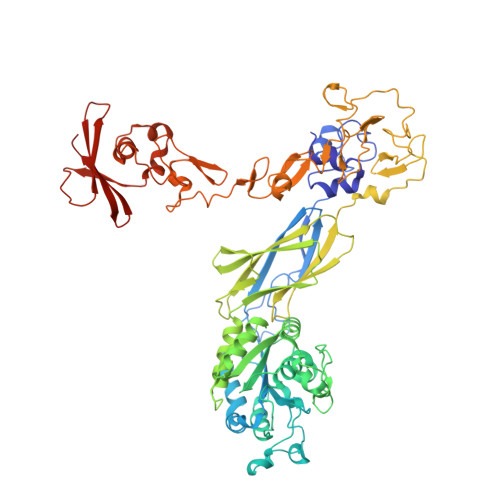
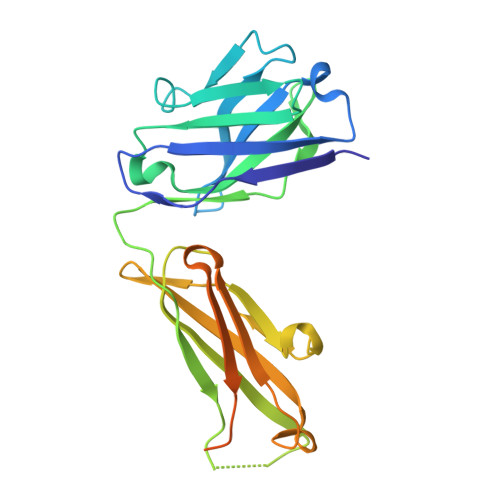
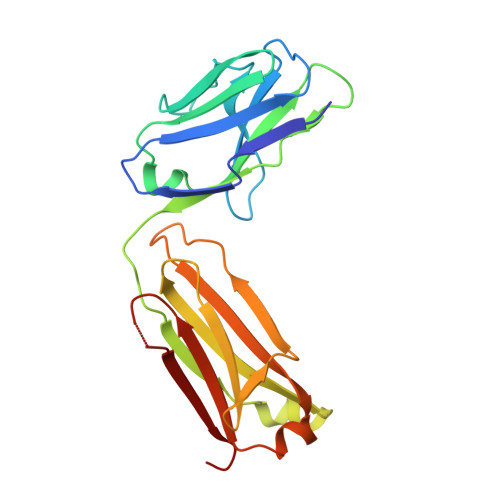
The Therapeutic Antibody LM609 Selectively Inhibits Ligand Binding to Human alpha V beta 3 Integrin via Steric Hindrance.
Borst, A.J., James, Z.M., Zagotta, W.N., Ginsberg, M., Rey, F.A., DiMaio, F., Backovic, M., Veesler, D.(2017) Structure 25: 1732-1739.e5
- PubMed: 29033288
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.09.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OPY, 6AVQ, 6AVR, 6AVU - PubMed Abstract:
The LM609 antibody specifically recognizes α V β 3 integrin and inhibits angiogenesis, bone resorption, and viral infections in an arginine-glycine-aspartate-independent manner. LM609 entered phase II clinical trials for the treatment of several cancers and was also used for α V β 3 -targeted radioimmunotherapy. To elucidate the mechanisms of recognition and inhibition of α V β 3 integrin, we solved the structure of the LM609 antigen-binding fragment by X-ray crystallography and determined its binding affinity for α V β 3 . Using single-particle electron microscopy, we show that LM609 binds at the interface between the β-propeller domain of the α V chain and the βI domain of the β 3 chain, near the RGD-binding site, of all observed integrin conformational states. Integrating these data with fluorescence size-exclusion chromatography, we demonstrate that LM609 sterically hinders access of large ligands to the RGD-binding pocket, without obstructing it. This work provides a structural framework to expedite future efforts utilizing LM609 as a diagnostic or therapeutic tool.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA.