Structure-Based Discovery and Optimization of Benzo[ d]isoxazole Derivatives as Potent and Selective BET Inhibitors for Potential Treatment of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC)
Zhang, M., Zhang, Y., Song, M., Xue, X., Wang, J., Wang, C., Zhang, C., Li, C., Xiang, Q., Zou, L., Wu, X., Wu, C., Dong, B., Xue, W., Zhou, Y., Chen, H., Wu, D., Ding, K., Xu, Y.(2018) J Med Chem 61: 3037-3058
- PubMed: 29566488
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00103
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
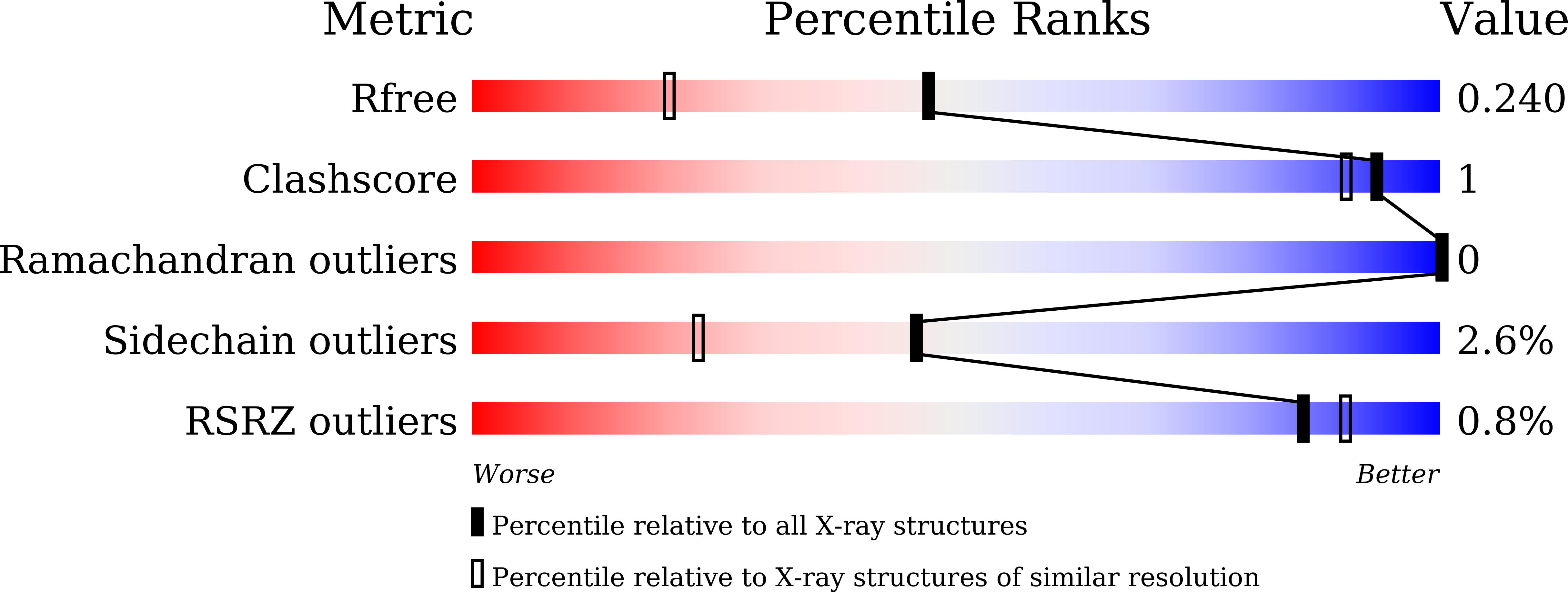
5Y8C, 5Y8W, 5Y8Y, 5Y8Z, 5Y93, 5Y94 - PubMed Abstract:
The bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) family proteins have gained increasing interest as drug targets for treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Here, we describe the design, optimization, and evaluation of benzo[ d]isoxazole-containing compounds as potent BET bromodomain inhibitors. Cocrystal structures of the representative inhibitors in complex with BRD4(1) provided solid structural basis for compound optimization. The two most potent compounds, 6i (Y06036) and 7m (Y06137), bound to the BRD4(1) bromodomain with K d values of 82 and 81 nM, respectively. They also exhibited high selectivity over other non-BET subfamily members. The compounds potently inhibited cell growth, colony formation, and the expression of AR, AR regulated genes, and MYC in prostate cancer cell lines. Compounds 6i and 7m also demonstrated therapeutic effects in a C4-2B CRPC xenograft tumor model in mice. These potent and selective BET inhibitors represent a new class of compounds for the development of potential therapeutics against CRPC.
Organizational Affiliation:
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Biocomputing, Joint School of Life Sciences, Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences ; Guangzhou Medical University , Guangzhou , China.